摘 要
本文主要研究成都地区教学建筑不同朝向适宜的外遮阳形式及尺寸优化设计。首先根据水平式与垂直式遮阳板尺寸计算公式,推导出多层水平遮阳、多层倾斜水平遮阳、多层垂直遮阳以及多层倾斜垂直遮阳的遮阳板尺寸计算公式。基于节能、采光及节材优化设计原则,在外遮阳尺寸理论计算基础上,采用数值模拟方法进一步优化外遮阳形式及遮阳构件尺寸。
本文主要研究结果如下:
(1)文中对两种计算依据下得到的不同遮阳构件尺寸的外遮阳形式进行模拟研究,结果发现南向以“充分遮阳线”对应的太阳高度角和方位角计算出的外遮阳尺寸是以“极端高温天气日”对应的太阳高度角计算出的外遮阳尺寸的三倍,能耗相差不大,且满足成都地区教学建筑采光要求;东、西向以“充分遮阳线”对应的太阳高度角和方位角计算出的外遮阳尺寸小于以“极端高温天气日”对应的太阳高度角计算出的外遮阳尺寸,虽然前者节能率稍高一点,但不满足成都地区教学建筑采光要求。因此,实际工程中可按极端高温天气日对应的太阳高度角和方位角进行遮阳构件尺寸设计优化。
(2)对建筑南向、东向和西向外遮阳优化设计进行模拟研究,综合考虑各影响因素,得到不同朝向最佳的遮阳方式与尺寸。①南向教室外窗宜采用水平式遮阳,其遮阳板尺寸为:遮阳板水平挑出 384mm,两端挑出 720mm,相对无外遮阳时节能率为1.01%。②东向教室外窗外遮阳优化设计模拟时,首先采用挡板式遮阳,虽然能降低总能耗,但是采光系数以及平均照度都不满足成都地区教学建筑的采光要求,因此东向不适合采用挡板式遮阳。接着采用多层水平遮阳板的外遮阳,当水平遮阳板为 3层时,在满足采光的前提下,室内能耗相对最小,然而水平遮阳板出挑长度仍较大,将水平遮阳板倾斜一定角度,虽能减少遮阳板出挑尺寸,但不能满足室内采光的需要。最后采用多层垂直遮阳板的外遮阳,综合考虑采光、节能及节材的因素,垂直遮阳板采用 8层,倾斜40°时最佳,此时的室内采光系数为 4.72%,平均照度为565lx,室内耗冷量为117.05k Wh/m2,耗热量为 65.62k Wh/m2,室内总能耗为 182.67k Wh/m2,相对无外遮阳时的节能率为 3.58%。
因此,东向教室外窗宜采用垂直遮阳板采用 8层,倾斜40°的外遮阳形式,具体尺寸为:垂直遮阳板出挑长度为 426mm,间距为675mm。③西向教室外窗外遮阳优化设计模拟时,首先采用挡板式遮阳,虽然能降低总能耗,但是其采光系数以及平均照度都不满足成都地区教学建筑的采光要求,因此西向也不适合采用挡板式遮阳。接着采用多层水平遮阳板的外遮阳,当水平遮阳板为5层时的外遮阳综合效果最佳,此时的室内采光系数为3.94%,平均照度为471lx,室内耗冷量为106.80k Wh/m2,耗热量为66.64k Wh/m2,室内总能耗为173.44k Wh/m2,相对无外遮阳时的节能率为2.66%。因此,西向教室外窗宜采用5层水平遮阳板的外遮阳,具体尺寸:水平板出挑长度为394mm,遮阳板间距为480mm。
本文的研究可为实际工程中外遮阳形式选择与尺寸优化提供参考,具有一定的工程意义。
关键词 : 教学建筑;外窗外遮阳设计;理论计算;数值模拟。
Abstract
This paper mainly studies the optimal design of exterior shading form and size for differentorientations of teaching buildings in Chengdu. Firstly, according to the size calculation formulaof horizontal and vertical shading, the size calculation formulas of multi-layer horizontalshading, multi-layer inclined horizontal shading, multi-layer vertical shading and multi-layerinclined vertical shading are deduced. Based on the optimization design principle of energysaving, lighting and material saving, and on the basis of theoretical calculation of exteriorshading size, numerical simulation method was adopted to further optimize exterior shadingform and exterior shading component size.

The main research results of this paper are as follows:
(1) Of the two kinds of calculation under different shading outer shading form of thecomponent size for simulation study, the results found that south to "full shade line" of the solaraltitude Angle and azimuth Angle corresponding to calculate the external blinds size based onthe extreme hot weather day outside of the solar altitude angles corresponding to calculate theshade size three times, energy consumption were similar,And meet the lighting requirements ofteaching buildings in Chengdu area;The external shading size calculated by the sun heightAngle and azimuth Angle corresponding to the "full shading line" in the east and west directionis smaller than that calculated by the sun height Angle corresponding to the "extreme hightemperature day". Although the former has a slightly higher energy saving rate, it does not meetthe lighting requirements of teaching buildings in Chengdu.Therefore, the size designoptimization of shading components can be carried out according to the sun altitude Angle andazimuth Angle corresponding to extreme high temperature days in practical engineering.
(2) The optimal shading design of the building in the south, east and west directions issimulated and studied. Considering the factors of energy consumption, lighting and materialsaving, the optimal shading method and size for different orientations are obtained.①Horizontal sunshade should be used for the outer window of the south-facing classroom.The size of the sunshade is 384mm horizontally picked out and 720mm at both ends. The energyrate is 1.01% when there is no external shading.②In the optimization design simulation of shading outside the windows of the east-facingclassroom, the baffle shading is firstly adopted. Although the baffle shading can reduce the totalenergy consumption, its lighting coefficient and average illumination do not meet the lightingrequirements of teaching buildings in Chengdu, so the baffle shading is not suitable for the east-facing classroom. When the number of horizontal visors is 3, the indoor energy consumption isrelatively minimum on the premise of satisfying the lighting. However, the length of thehorizontal visor is still large. By tilting the horizontal visor at a certain Angle, the size of thevisor can be reduced, but it cannot meet the needs of indoor lighting. Finally, the externalshading with multi-layer vertical sun visor is adopted. Considering the factors of lighting,energy consumption and material saving, the external shading with 8-layer vertical sun visor isadopted. The best shading is when the sun visor tilts 40°. at this time of indoor daylightingcoefficient was 4.72%, the average intensity of illumination for the 565 lx, indoor coldconsumption is 117.05 k Wh/m2, heat consumption of 65.62 k Wh/m2, indoor total energyconsumption of 182.67 k Wh/m2, relative without external blinds the energy-saving rate of3.58%. Therefore, the external window of the east facing classroom should adopt the externalsun shading with 8 layers of vertical sun visors, with a tilt of 40°. The specific size is as follows:the overhanging length of the vertical sun visors is 426mm, and the spacing is 675mm.③In the optimization design simulation of shading outside the window of the west facingclassroom, baffle shading is firstly adopted. Although baffle shading can reduce the total energyconsumption, its lighting coefficient and average illumination do not meet the lightingrequirements of teaching buildings in Chengdu, so baffle shading is not suitable for the westfacing. Then, the external shading with multi-layer horizontal sunshade was adopted. When theexternal shading with five-layer horizontal sunshade was the best, the indoor lightingcoefficient was 3.94%, the average illumination was 471lx, the indoor cooling consumptionwas 106.80k Wh/m2, the heat consumption was 66.64k Wh/m2, and the total indoor energyconsumption was 173.44k Wh/m2, and the energy saving rate was 2.66% compared with thatwithout external shading. Therefore, the exterior shading of 5 layers of horizontal sun visorsshould be used for the exterior window of the western-facing classroom. The specificdimensions are as follows: the overhanging length of the horizontal board is 394mm, and thespacing of the sun visors is 480mm.
The research in this paper can provide reference for the selection of shading forms andsize optimization in practical engineering, which has certain engineering significance.
Key Words: Teaching building; Shading design outside the window; The theoreticalcalculation;Numerical simulation 。
1、绪论
1.1、研究背景。
1.1.1、我国建筑能耗现状。
近年来,随着经济高速发展和生活水平迅速提高,同时人口急剧增长,导致能源消耗越来越严重。
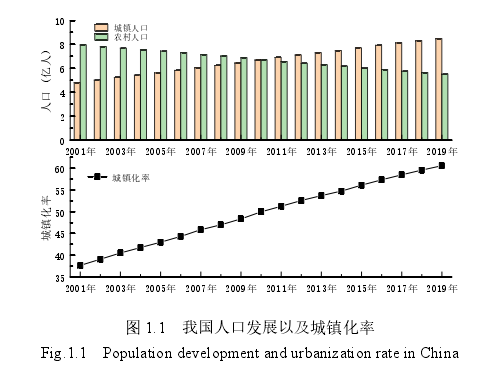
2001年至2019年我国城镇化高速发展,大量人口由乡村向城镇转移,城镇居民人口数从2001年的4.81亿迅速增长到8.48亿,农村人口数从2001年的7.96亿降低到5.52亿,城镇率从2001年的37.7%增长到60.6%[1],如图1.1所示。
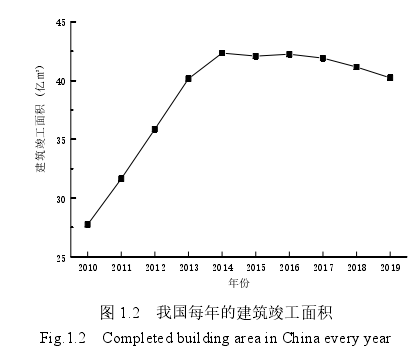
城镇化的快速发展使得我国建筑业规模不断扩大,城乡面积大幅增加。据国家统计局公布的每年建筑竣工面积统计数据显示:我国建筑每年的竣工面积从2010年的27.75亿m2增加到2019年的40.23亿m2[1],如图1.2所示。
2014年以前,我国每年的建筑竣工面积增长迅速,自2014年至今,我国每年的建筑竣工面积已连续多年的小幅下降,但基本稳定在40亿m2[1]。每年大量的建筑竣工使得我国建筑面积总量不断增加,据资料显示,2018年我国建筑面积总量约为601亿m2,其中:城镇住宅建筑面积为244亿m2,农村住宅建筑面积为229亿m2,公共建筑面积约为128亿m2[2]。
建筑业迅猛发展,使得建筑面积不断增加,因此造成了巨大能源消耗。建筑能源消耗主要包括建筑建造能耗(建筑建造过程中所导致的从原料开采、建材生产、运输以及现场施工所产生的能源消耗)以及建筑使用过程中的建筑运行能耗两大部分。根据文献[2]的资料显示:
2018年我国建筑运行能耗和建筑建造能耗占总能耗的37%,其中,建筑建造能耗占比14%,建造运行能耗占比23%。建筑运行能耗包括建筑物通风、空调、供暖、照明、和其他为了实现建筑各项服务功能所产生的能耗,一直伴随建筑物使用过程而发生。随着我国逐渐进入城镇化新阶段,建设速度放缓,建筑的排放和运行能耗将成为更大的部分。因此,建筑运行能耗成为建筑节能任务中主要的关注点。
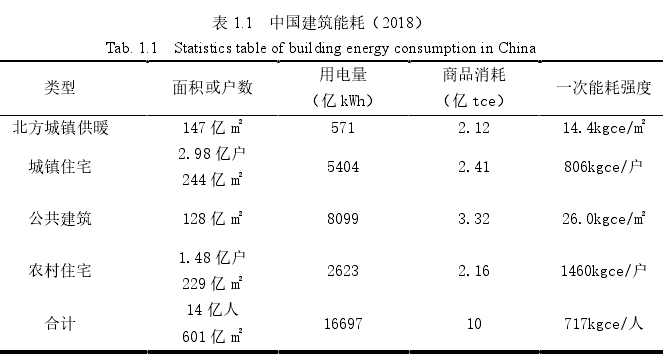
根据能耗特点,我国民用建筑运行能耗可分为公共建筑用能、城镇住宅用能、北方城镇供暖用能、以及农村住宅用能四类[2],各部分能耗如表1.1所示。从表1.1中可以看出,公共建筑总能耗(不含北方供暖)为3.32亿吨标准煤,占建筑总能耗的33%,其面积约占建筑面积总量的1/5,所以从单位面积能耗强度来看,公共建筑能耗强度却是四类建筑用能强度最高的[2]。可见,公共建筑的节能迫在眉睫。
【由于本篇文章为硕士论文,如需全文请点击底部下载全文链接】
1.1.2 、我国高校建筑能耗现状.
1.1.3 、教学建筑外遮阳的必要性
1.2 、研究目的及意义
1.2.1、 研究目的
1.2.2、 研究意义
1.3、国内外研究现状
1.3.1、 国内研究现状.
1.3.2、 国外研究现状.
1.3.3 、文献评述
1.4 、研究内容及技术路线
1.4.1、 研究内容
1.4.2、 技术路线
2、建筑外遮阳相关概述.
2.1、外遮阳的分类.
2.1.1、按产品类型分类 .
2.1.2、按遮阳基本形式分类.
2.1.3、按操作方式分类.
2.14、按遮阳材料分类.
2.2、外遮阳设计的依据
2.2.1、建筑气候 .
2.2.2、房间功能.
2.2.3、窗口朝向
2.3、建筑外遮阳对节能和室内环境的影响
2.3.1、建 筑外遮阳对节能的影响
2.3.2、建筑外遮阳对室内光环境的影响
2.4、本章小结
3、成都地区气候环境与教学建筑特点研
3.1、成都地区气候环境
3.1.1、太阳辐射
3.1.2、温度分布
3.13、湿度分布
3.2、教学建筑特点
3.2.1、教学空间
3.2.2、室内热扰
3.2.3、建筑能耗
3.3、成都地区教学建筑遮阳现状
3.3.1、调研目的与调研内容.
3.3.2、调研结果分析.
3.3.3、成都地区教学建筑遮阳现状及存在的问题.
3.4、本章小结
4、成都地区教学建筑外窗外遮阳初步设计
4.1、成都地区教学建筑遮阳日期与时间
4.1.1、成都地区教学建筑设置外遮阳的条件.
4.1.2、成都地区教学建筑遮阳日期与时间
4.2、成都地区遮阳日期的太阳位置
4.2.1、太阳赤纬角
4.2.2、太阳时角
4.2.3、太阳高度角
4.2.4、太阳方位角
4.2.5、成都地区遮阳期不同日期不同时刻的太阳位置
4.3、遮阳板设计的基本公式及推导
4.3.1、水平式遮阳
4.3.2、垂直式遮阳
4.3.3、挡板式遮阳
4.35、多层倾斜水平遮阳.
4.3.6、多层垂直式遮阳
4.3.7、多层倾斜垂直式遮阳
4.4、遮阳板尺寸初步计算
4.4.1、遮阳板尺寸计算依据
4.4.2、遮阳板尺寸初步计算
4.5、本章小结.
5、成都地区教学建筑外窗外遮阳优化设计模抑研.
5.1、外遮阳优化设计原则与方法
5.1.1、外 遮阳优化设计原则
5.1.2、外遮阳优化设计方法.
5.2、模型建立及外遮阳效果评价指标
5.2.1、模 拟软件简介.
5.2.2、建立物理模型.
5.2.3、模拟参数设置,
5.2.4、外遮阳评价指标.
5.3、南向遮阳优化设计
5.3.1、遮阳尺寸优化选择.
5.3.2、不同热工性能的外窗外遮阳对室内能耗和采光影响
5.3.3、南向模拟结果总结.
5.4、东向遮阳优化设计
5.4.1、采用挡板 式遮阳
5.4.2、采用多层水平遮阳板的外遮阳.
5.4.3、采用多层垂直遮阳板的外遮阳.
5.4.4、东向模拟结果总结.
5.5、西向遮阳优化设计
5.5.1、采用挡板式遮 阳.
5.5.2、采用多层水平遮阳板的外遮阳
5.5.3、西向模拟结果总结
5.6、本章小结
6、结论
本文以成都地区为例,对成都地区教学建筑外遮阳进行设计研究。得出主要结论如下:
(1)在水平式与垂直式遮阳板尺寸计算公式的基础上,推导出了多层水平式、多层倾斜水平遮阳、多层垂直遮阳以及多层倾斜垂直遮阳的遮阳板尺寸计算公式。
(2)综合考虑室内能耗、采光以及节材等因素,比较分析两种计算依据得到的外遮阳尺寸,得到实际工程中按极端高温天气日对应的太阳高度角和方位角进行遮阳构件尺寸设计优化的方法。
(3)对建筑南向、东向和西向的外遮阳优化设计进行模拟研究,综合考虑能耗、采光和节材等因素,得到不同朝向下的最佳遮阳形式与尺寸。
①南向教室外窗宜采用水平式遮阳,其遮阳板尺寸为:遮阳板水平挑出384mm,两端挑出720mm。相对无外遮阳时节能率为1.01%。
②东向教室外窗宜采用8层垂直遮阳板的外遮阳,遮阳板倾斜40°,具体尺寸为:垂直遮阳板出挑长度为426mm,间距为675mm。相对无外遮阳时节能率为3.58%。
③西向教室外窗宜采用5层水平遮阳板的外遮阳,具体尺寸:水平板出挑长度为394mm,遮阳板间距为480mm。相对无外遮阳形式时节能率约为2.66%。
参考文献.
[1]国家统计局.2020中国统计年鉴[M].北京:中国统计出版社,2020.
[2]清华大学建筑节能研究中心建筑节能年度发展研究报告2020[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2020.
[3]清华大学建筑节能研究中心中国建筑节能年度发展研究报告2018[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2018.
[4]杨宇乐.武汉地区既有高校教学建筑外遮阳优化设计研究[D].青岛理工大学2020.
[5]王雅静.教学建筑外遮阳的复合化设计研究[D].重庆大学2015.
[6]岳鹏.建筑遮阳技术手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2014.
[7]涂逄祥.中国建筑遮阳技术[M].北京:中国质检出版社2015.
[8]简毅文,王苏颖,江亿.水平和垂直遮阳方式对北京地区西窗和南窗遮阳效果的分析[J].西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, (03): 212-217.
[9]张杰吴保华.水平式遮阳构件尺寸的计算研究[J].四川建筑科学研究, 2005, (01): 119-120+ I27.
[l0]朱燕燕,杨坤丽,韦延年.浅析建筑构件遮阳系数确定[].四川建筑科学研究, 2007, (02): 143-l 45.
[1]张建海,姚健,周燕,等.关于水平遮阳板节能最优化尺寸的探讨一-- 以宁波地区为例[J]门窗,2008(03):35-38
[12]陈震,何嘉鹏.南京地区南窗外遮阳构件尺寸研究[ ].新型建筑材料,2009 ,36(06):52-55.
[13]唐慧华.建筑遮阳构件的结构设计[J].建筑设计管理2015,3204)68-69.
[14]李吴,刘梵思.夏热冬冷地区多层建筑屋顶构件节能优化设计---以百叶型遮阳构件为例[J].湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 2018, 27(01 ): 28-32.
[15]李鑫.湖南地区建筑遮阳系统设计方法研究[D].湖南大学2005.
[l6]朱燕燕.夏热冬冷地区建筑遮阳系统设计及其节能评价[D].西南交通大学2007.
[17]石丹.居住建筑窗户外遮阳优化设计研究[D]重庆大学,2008.
[18]权公恕、夏热冬冷地区建筑外遮阳与建筑整合设计研究[D].浙江大学,2008.
[19]张连飞.天津地区办公建筑窗口外遮阳设计研究[D]天津大学2008.
[20]李斌.我国南方地区村镇住宅外窗水平外遮阳设计研究[D]湖南大学,2010.
[21]胡深,冉茂宇,袁炯炯,等关于居住建筑遮阳优化设计的探讨[].建筑科学2010,26(12);88-91.
[22]朱春..上海地区住宅建筑外遮阳设计优化研究[J].绿色建筑2012,4(05):36-39.
[23]陈勇明.夏热冬暖地区建筑外遮阳与建筑一体化设计研究[D]重庆大学2014.
[24]王梦滢.教育建筑遮阳设计研究[D].青岛理工大学2016.
[25]杨锦春.徐州市办公建筑南向窗口遮阳优化设计研究[D].中国矿业大学2017
[26]杜峰,刘辉.建筑的天然采光与遮阳设计[D.住宅科技,2005(12 ):25-27.
[27]汤民.百叶外遮阳对建筑自然通风影响的研究[D].同济大学,2007.
[28]张海遐,陈浩,金瑞娟,等.活动式建筑遮阳设施对南京地区居住建筑室内自然通风的影响[J].江苏建筑2009(05):87-88.
[29]李跃群.遮阳构件对室内自然通风影响的研究[D]华南理工大学2010.
[30]费双.建筑遮阳条件下的自然采光设计策略[J]中外建筑201 1(1 1);:103- 105.
[31]孙楠.基于自然采光与通风的绿色遮阳技术研究[D]山东建筑大学2015.
[32]徐菁.西安地区南向窗口不同遮阳形式对室内采光的影响[J].建筑节能, 2016, 4406): 61-64.
[33]谢斌,胡望社,姚建政.基于Ecotect 的建筑遮阳采光节能设计优化策略[].建筑节能, 2017,45(12): 44-50.
[34]庄连飞.百叶外遮阳对建筑夏季自然通风与热舒适的影响研究[D].南京师范大学2018.
[35]马蕊现代家居智能化发展及应用研究[D].北方工业大学2014.
[36]熊伟.玻璃幕墙建筑动态百叶遮阳板的算法设计研究[D].西华大学,2018.
[37]黄永.智能百叶与建筑遮阳[]华中建筑2003(05);77-78.
[38]任晓强智能楼宇遮阳控制系统的研究[D].北京林业大学2007.
[39]袁小平.电动遮阳板自动控制系统的研制[D]天津大学2007.
[40]熊爱民,谢轩等.基于人工神经网络模型的智能遮阳控制系统[J].电子科技:2013,26(5)47 49.
[41]郭鹏伟.基于智能控制的建筑外遮阳节能系统研究[D].武汉轻工大学,2014.
[42]陈展,唐国安浅谈智能建筑中的智能遮阳系统[D.中外建筑,2009(07 ):58-59.