摘 要
近年来建筑工业化和机器人化成为建筑行业发展的一大趋势。我国是瓷砖大国,瓷砖使用量位居世界第一,瓷砖铺贴需要自动化,开发瓷砖铺贴机器人成为目前需要迫切解决的一个问题。瓷砖铺贴机器人模仿人工瓷砖铺贴过程,实现瓷砖的自动化铺贴。该机器人由检测单元、机械手运动单元、控制单元和瓷砖仓储等构成,机器人通过检测单元得到瓷砖的位置信息,然后通过控制单元控制机械手运动,运动包括瓷砖拾取、抹胶(或砂浆)、放置和震平。显然,位置检测是机器人的一个极为重要的组成部分,其检测精度、速度都将影响到瓷砖铺贴机器人的铺贴精度和速度。

本文主要对实验室研制的 CR1 型瓷砖铺贴建筑机器人检测单元进行研究,主要内容包括:瓷砖空间定位的一般性方法、非接触激光定位方法、非接触激光定位方法测量精度及其误差分析等。物体空间定位方法包括视觉定位、红外定位、激光定位及 GPS 定位等,针对建筑场景,检测方法需要满足建筑环境复杂、光照强度差、工作环境多样性的特点,因此采用激光定位系统进行瓷砖空间位置检测,它具有非接触、不受光照条件影响、快速识别等优点,可以满足复杂建筑环境下瓷砖位置的测量要求。瓷砖定位系统安装有 2 个激光测距传感器,可检测不同状态下的瓷砖边缘及高度位置,通过二维平面的定位算法,扩展到瓷砖的三维空间定位算法,将二维平面得到的位置信息进行融合,得到瓷砖的空间形态进而得到瓷砖的空间位置。本文对位置检测方法及定位算法进行了研究。
本文进一步研究了基于激光测距传感器的检测精度及其影响因素问题。激光测距传感器的移动速度对检测精度有重要影响。通过对不同速度下的实验研究和数据分析,获得了在保证速度最快的情况下激光测距传感器的参数设置,并使其检测精度最高,从而保证瓷砖铺贴机器人的铺贴效率。文章对检测数据、检测精度及其误差进行了分析。最后,本文对上述提出的测量方法、数据分析算法在我们实验室研制的 CR1 瓷砖铺贴机器人进行实际编程运行。经验证,本文提出的方法正确,实验结果在瓷砖铺贴机器人瓷砖铺贴要求的精度范围以内,所涉及的算法也能有效抑制激光测距传感器重复性误差等问题。
关键词: 瓷砖铺贴;机器人;激光定位;空间定位。
Abstract
In recent years, construction industrialization and robotization have become a major trend in the development of construction industry. China is a big country of ceramic tile, ceramic tile usage amount ranks the first in the world, ceramic tile shop sticks need automation,development of robot of ceramic tile shop sticks a problem that needs to be solved urgently at present. Tile paving robot imitates artificial tile paving process to realize automatic tile paving.The robot consists of a detection unit, a manipulator motion unit, a control unit and a ceramic tile storage unit. The robot obtains the position information of the ceramic tile through the detection unit, and then controls the motion of the manipulator through the control unit, which includes pickingup the ceramic tile, applying glue (or mortar), placing and levelingthe ceramic tile. Obviously, the position detection is an extremely important part of the robot, and its detection precision and speed will affect the tile paving robot's paving precision and speed.
In this paper, the detection unit of CR1 tile paving construction robot developed in the laboratory is studied, which mainly includes: general method of tile space positioning, non-contact laserpositioning method,measurement precisionanderror analysis ofnon-contact laser positioning method. Orientation of object space positioning methods including visual and infrared and laser positioning and GPS positioning, etc., aiming at building scene, detection methods need to meet the complex construction environment, the characteristics of light intensity difference, work environment persity, so the laser positioning system for ceramic tile spatial location detection, it has the non-contact, is not affected by light conditions, and the advantages of rapid identification, can satisfy the measurement of complex constructionenvironment of ceramic tile position requirements. Ceramic tile has two laser ranging sensor positioning system installation, different stages of ceramic tile edge can be detected and high position,throughthelocalizationalgorithmofthetwo-dimensionalplane,extendedtothethree-dimensional localization algorithm of ceramic tile, location information obtained by the 2 dplane fusion, the space form of ceramic tile and then get the space position of ceramic tile. In this paper, the location detection method and location algorithm are studied.
This paper further studies the detection accuracy and its influencing factors based on laser ranging sensor. The moving speed of laser ranging sensor has an important effect on the detection accuracy. Through the experimental research and data analysis at different speeds, the parameters of the laser ranging sensor are set with the highest speed and the highest detection accuracy, so as to ensure the efficiency of the robot. In this paper, the detection data, detection precision and error are analyzed. Finally, the measurement method and data analysis algorithm proposed above are programmed and run in the CR1 tile paving robot developed in our laboratory. It is proved that the method presented in this paper is correct, the experimental results are within the precision range required by the tiling robot, and the algorithm involved can effectively suppress the repeatability error of laser ranging sensor.
Keywords: Ceramic tile shop is stuck;The robot;Laser positioning;Spatial orientation。
第1章 绪论
1.1 、研究背景。
1.1.1、 研究背景及意义。
建筑业作为历经人类历史时间最长的工程实践活动,与人类的生活息息相关,好的建筑风格能给人以美的享受,过硬的建筑质量能给人安全感,优良的建筑环境能带给人舒适的感觉,而先进可靠的建筑手段则是改善与提高这些的关键因素[1]。整体建筑中影响建筑美感好坏的其中一个因素为瓷砖铺贴,随着瓷砖产量的不断增长,瓷砖铺贴的技术要求也随之提高。加之我国是瓷砖生产大国,每年的全国瓷砖产量达到 100 多亿平方米,近年来,瓷砖铺贴工人的人工费用也在逐年增长,截止到 2019 年,平均 1 平方米的瓷砖铺贴工人费为 50 元左右,如果这些瓷砖都由人工铺设,将花费大量的人工成本[2-4]。
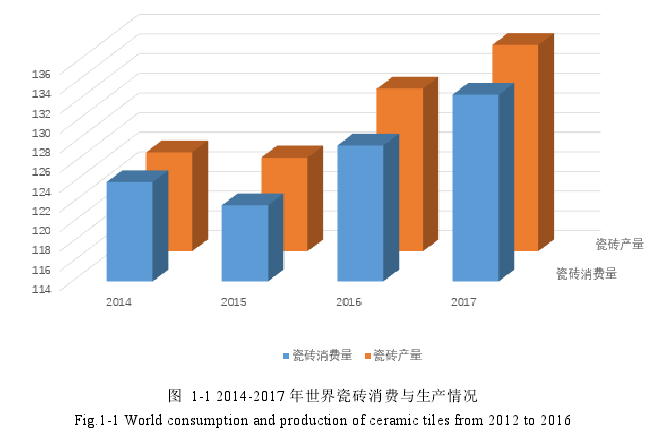
从 2014-2017 年世界瓷砖消费与生产情况可以看出,世界整体的瓷砖消费水平是逐年上升的,增长率至少 1%/年,随着瓷砖消费的增长,人工成本也将逐年攀升。瓷砖铺贴机器人及瓷砖精确空间定位的研究将致力于解决建筑行业瓷砖铺贴、人工成本过高、建筑材料浪费及人工铺贴慢等问题,因而瓷砖铺贴机器人在建筑行业有着非常大的实际意义和广泛的应用前景。
瓷砖用量的增长及铺贴技术要求的提高,意味着瓷砖铺贴将由人工铺贴走向工业化、智能化铺贴,瓷砖铺贴工业化最重要的为瓷砖铺贴方式的转换,铺贴方式转换过程中最重要的要数将人眼感官瓷砖铺贴位置的动作转换为工业上的瓷砖空间定位技术,这一技术的转换将推动瓷砖铺贴机器人的发展。
人工铺贴时,处理好地面后,将水泥黄砂浆均匀的抹到瓷砖背面,保证每个瓷砖抹匀。按照顺序依次铺贴,铺贴好后用橡皮锤轻轻敲实,用水平尺查看瓷砖是否平整,瓷砖铺贴 2-3 小时后,使用白水泥或美缝剂勾缝。缝隙需要填充严实饱满,最后将多余涂料擦去。人工铺贴时无法靠感官保证瓷砖定位,故采用白十字保证瓷砖间的缝隙,如图1-2 所示,此定位方式费时费力,白十字的安装会浪费大量时间,降低瓷砖铺贴效率,因此需要工业化的瓷砖定位方式。
瓷砖铺贴机器人铺贴时,将瓷砖放到瓷砖库内,首先对已铺贴完成的瓷砖进行定位,然后机器人利用喷浆系统将瓷砖胶喷涂到待铺贴位置,再由机器人抓取瓷砖库内的瓷砖将其铺贴到待铺贴位置上。基于瓷砖铺贴机器人的瓷砖空间定位,总的来说是利用定位系统,通过提供测量手段对目标瓷砖定位扫描,来实现瓷砖的空间定位[5]。

【由于本篇文章为硕士论文,如需全文请点击底部下载全文链接】
1.2 、国内外研究现状.
1.2.1、 国外研究现状
1.2.2 、定位技术研究现状
1.2.3 、激光测距传感器研究现状
1.3、 本章小结.
第 2 章 瓷砖空间定位测量系统组成及定位原理
2.1 、瓷砖定位系统组成.
2.1.1、 激光测距传感器
2.1.2、 激光控制器
2.1.3、 机器人系统
2.1.4、 Beckhoff 嵌入式主控制器.
2.2 、激光定位系统的定位方法及原理.
2.2.1、 定位方法设计
2.2.2、 定位系统的物理定位原理
2.2.3 、定位系统的检测原理
2.3、 本章小结.
第 3 章 瓷砖空间定位系统设计.
3.1 、不同状态的瓷砖定位分析.
3.1.1、 激光测距传感器的定位环境分析
3.1.2、 瓷砖定位目标分析
3.2 、激光测距传感器定位系统的硬件部署.
3.3 、激光测距传感器定位系统的软件平台.
3.4 、本章小结
第 4 章 瓷砖定位系统定位算法分析与设计
4.1 、瓷砖位置算法分析.
4.1.1、 数据预处理
4.1.2 、瓷砖平面方程的计算
4.1.3 、瓷砖中心和偏转角的计算
4.2 、三维空间定位算法设计.
4.2.1、 瓷砖定位的空间坐标系建立
4.2.2、 空间坐标系转换
4.2.3、 三维空间定位分析
4.3 、本章小结.
第 5 章 机器人仿真实验与瓷砖定位实验
5.1、 机器人仿真实验.
5.2 、激光重复性实验.
5.3、 激光中断实验.
5.4 、激光最优检测速度实验.
5.5 、瓷砖空间定位实验及定位结果.
5.5.1、 激光检测过程
5.5.2、 瓷砖定位铺贴实验结果
第6章 总结
本文介绍了瓷砖铺贴机器人的研究背景以及现有的物体定位方法,通过复杂建筑环境下对定位系统的需求分析,选定激光测距传感器进行瓷砖定位检测,并根据其检测特点完成瓷砖定位系统的硬件设计与部署。分别在智能瓷砖铺贴机器人的末端和移动平台外侧各安装 1 个激光测距传感器,分别对不同目标瓷砖进行检测,得到不同目标瓷砖的位置信息,最后将 2 个激光测距传感器的检测数据进行融合,最终得到待铺贴瓷砖的铺贴位置。
针对激光与瓷砖的定位特点,本文采用基于空间几何的定位策略,借助二维、三维的空间定位特点,确定了瓷砖空间定位算法,并对定位算法流程进行了详细的介绍与分析。
基于 MATLAB 进行 UR 机器人仿真实验时,对机器人的移动坐标进行多次更改,并将仿真数据与实际数据进行比较,验证机器人移动误差在可行性范围内。
本文通过激光测距传感器自身的检测特点研究,建立针对激光测距传感器的实验方案,探究不同情况下不同参数对瓷砖定位精度的相对应的影响。
本文通过对瓷砖定位系统的整体研究及对应实验数据得到以下结论:
1.通过对现有定位系统应用场景及其定位特点的分析,发现视觉系统对光照条件的变化有明显的反应,尤其是针对建筑环境下的定位工作,相较于视觉定位,激光定位有较强的环境适应性。从定位精度上看,激光定位系统的定位精度可完全达到建筑行业瓷砖铺贴精度。
2.针对激光的特点和需要检测的瓷砖信息进行算法设计,并考虑过程中影响定位精度的因素,在瓷砖定位的实现过程中进行误差修正,保证了瓷砖的定位精度。
3.激光传感器本身存在检测性误差,即重复性误差,通过重复性误差的大量实验数据得出,4 个基准点的重复性检测曲线图存在一定的共性。检测数值曲线呈上升趋势,整体出现正向误差的比例较高,在第 12 次对同一点检测时其检测数据达到检测误差的正高峰,数据过滤掉的可能性最高,在前 5 次检测时的正确率最高。
4.在对中断信号的实验检测中,要在机器人与激光传感器的配合下得到实验数据,通过实验可以看出,控制器读取的激光测距传感器的中断信号也存在一定的规律,在某一时刻激光传感器的数据会迅速增大,此点便是激光开始检测到瓷砖的点,中断信号也应从此刻读取。
5.整体实验分析完毕之后,便是结合修正过的实验算法和程序进行瓷砖铺贴实验,经实验可得,实验得出的误差可提高瓷砖铺贴的精度,整个瓷砖铺贴机器人的铺贴精度符合建筑行业的瓷砖铺贴标准。
参考文献.


