摘 要
随着近些年我国新零售和社区零售等商业模式的大范围铺开,生鲜农产品的消费需求越来越旺盛,与此同时,消费者对于生鲜农产品也更加注重质量和新鲜度,但是目前我国冷链物流配送体系仍然存在一定的不足,在配送过程中存在货损较大以及配送时间安排不合理等问题。本文以Y连锁超市企业为研究对象,针对Y企业在生鲜农产品配送过程中存在的配送路线经验性选择较强、对门店期待送达时间重视不够和生鲜农产品货损较大等问题进行分析并以此建立数学模型,使得Y企业能够明确在配送过程中的各项成本因素,帮助企业确定合理的配送路线,降低配送成本。
本文的主要研究内容如下:
通过收集整理现有的有关生鲜农产品配送路径优化问题的相关资料,分析Y企业目前在产品配送过程中存在的问题,确定影响配送过程的各项成本因素,将生鲜农产品货损成本和企业各门店的时间窗成本充分考虑,通过简化实际情景建立符合Y企业生鲜农产品从配送中心到门店运输和服务实际过程的配送成本模型并确定目标函数和约束条件。
在求解Y企业配送优化模型时,首先使用遗传算法和人工蜂群算法对模型进行求解,然后使用一种在人工蜂群算法侦查蜂阶段引入遗传算法的交叉、变异和选择思路对人工蜂群算法进行改进的混合算法对Y企业配送优化模型进行求解,提升算法的搜索能力,使得改进算法能够求解得到更优的配送方案。
利用Y连锁超市企业分布在北京市的50家门店数据进行算例分析,通过对比验证改进后的遗传-人工蜂群算法的性能提升,并确定Y企业配送中心的各车辆的配送路线,然后分别对Y企业在日常经营过程中可能发生变化的门店需求量、运输车辆行驶速度和生鲜农产品服务系数进行灵敏度分析,分析各个因素变化对配送总成本的影响,并根据相应的分析结果对Y企业提出管理见解。
关键词 : 车辆路径优化;生鲜农产品;货损成本;软硬时间窗;人工蜂群算法。
ABSTRACT
With the widespread spread of new retail and community retailing business models in China overthe recent years, the consumer demand for fresh agricultural product is becoming more and moredemanding, at the same time, consumers lay emphasis on the quality and freshness of freshagricultural products distributed, but there are still some shortcomings in China's cold chain logisticsand distribution system, there are some problems such as large damage and unreasonabledistribution time arrangement. In this paper, Y supermarket chain enterprises as the research object,for Y enterprises during the delivery process of fresh agricultural products existing in the distributionroute experience of strong selection and the store expected delivery time attention is not enough toanalyze and establish a mathematical model, so that Y enterprises can clear the distribution processof various cost factors, to help enterprises determine a reasonable distribution route and reducedistribution costs.
The main research contents of this paper are as follows:
By aggregating and separating the available information on the path optimization of thedistribution of fresh agricultural products, analyzing the extant problems of Y enterprises in theprocedure of product distribution, determining the cost factors affecting the distribution process,taking the cost of loss of fresh produce and the cost of client time window into consideration, bystreamlining the actual situation to establish a cost model in line with the actual procedure of Yenterprise fresh agricultural products from distribution center to store transportation and service anddetermining the constraints and parameters.
When solving Y enterprise distribution optimization model, the first to use genetic algorithm andartificial colony algorithm to solve the model, and then use the artificial bee colony algorithm scoutsstage idea about selecting the introduction of the crossover and mutation of genetic algorithm andhybrid algorithm for artificial bee colony algorithm was improved to Y enterprise distributionoptimization model for solving, improve algorithm search ability, the improved algorithm is able toobtain a better distribution scheme.
The data of 50 stores of Y supermarket chain distributed in Beijing were used for example analysis.

Through comparison, the performance improvement of the improved genetic and artificial beecolony algorithm was verified, and the distribution routes of each vehicle in the distribution centerof Y were determined. Then, the sensitivity analysis of Y's store demand, transportation vehiclespeed and fresh agricultural product service coefficient that may change in the daily operationprocess is carried out, and the influence of each factor change on the total distribution cost isanalyzed, and management opinions are put forward for Y according to the corresponding analysisresults.
KEY WORDS : Vehicle routing problem; Fresh agricultural products; The cost of damage;Soft and hard time window; Artificial bee colony algorithm 。
第1章 绪 论
1.1、研究背景。
近年来,随着我国国民经济的快速持续发展,人民群众的物质生活水平越来越高,中国的城镇化率从1990年的26.4%提升至2019年的60.60%,城镇化率的提升带动了我国生鲜农产品消费需求的日益增加,2019年我国生鲜农产品市场交易规模达2.04万亿元,同比增长6.8%,呈现高速增长态势。虽然2020年受到突如其来的新冠肺炎疫情影响,但是由于受到群众居家办公等工作方式的影响,社区团购等成为新的商业发力点,在全国各城市大范围铺开,助力生鲜农产品的交易规模同比增长5.9%,达到2.16万亿元。
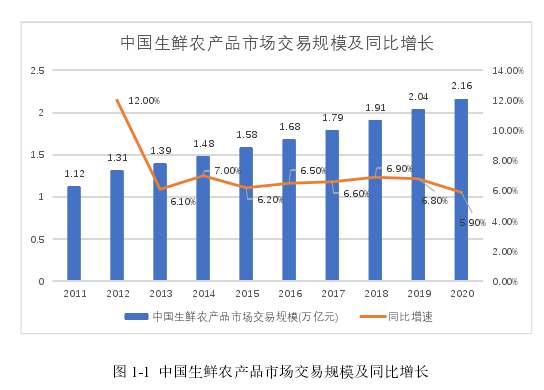
伴随着生鲜农产品消费数量的增加,广大消费者对生鲜农产品消费的关注点逐渐转向新鲜度、购买便捷性和食品安全性等方面。因此,承载以上关注点的农产品冷链物流也得到了相应的重视,但是我国与农产品配送向配套的冷链物流运输体系却没有完整建立。首先,我国目前运行的冷藏保温车数量较少,且冷藏保温车辆标准不统一。根据中国物流与采购联合会冷链委员会数据,冷藏保温车保有量仅占全国货运汽车保有量的0.4%,平均每1.5万人拥有1台冷藏车,而美国平均不到500人就拥有1台冷藏车,由于冷藏车的不足和质量较低,导致我国生鲜农产品运输中货损率达到10%~20%。其次,冷链车辆使用过程不规范,存在“断链”问题[1],例如一些企业在运输过程中,使用不达标的冷藏车进行配送,或人员不按照标准化流程操作导致冷链物流断链。最后,冷链物流设施布局不完整[2],在农村地区以及城市“最后一公里”等农产品运输关键环节中存在冷链物流设施缺乏、生鲜农产品直接采用常温运输等情况。
结合目前生鲜农产品销量的爆发式增长,Y连锁超市企业也加入到与各大电商平台和线下超市的竞争之中,生鲜农产品的营业收入连年递增,但是Y企业由于成立时间较短,伴随着旗下各个门店生鲜农产品需求量的增加,其管理经验缺乏、配送成本评估不合理和产品配送路线选择经验性较强等问题逐渐暴露,配送中心在为其门店进行配送时没有合理的配送路径,使得配送成本持续维持在较高水平,成为限制企业利润增长的重要原因之一。为实现Y企业生鲜农产品销售量增长目标,降低配送成本,同时提高其各个门店的满意度,为Y企业的配送中心制定合理的配送路线成为其必须面对的问题。
【由于本篇文章为硕士论文,如需全文请点击底部下载全文链接】
1.2、 研究目的与选题意义.
1.2.1 、研究目的
1.2.2 、选题意义.
1.3、主要研究内容及技术路线图.
1.3.1 、主要研究内容.
1.3.2、技术路线图
1.4、研究方法与创新点.
1.4.1、 研究方法.
1.4.2 、论文创新点
1.5、本章
第2章 相关理论基础及其文献综述
2.1、关于生鲜农产品冷链物流相关文献综述.
2.1.1、生鲜农产品冷链物流概念.
2.1.2、生鲜农产品冷链物流特点
2.2、车辆路径优化问题相关文献综
2.2.1、车辆路径优化问题相关研
2.2.2、带时间窗的路径优化问题研
2.2.3、生鲜农产品配送车辆路径优化问题研.
2.3 、路径优化问题求解算法相关综述.
2.3.1、路径优化问题求解算法分类.
2.3.2、路径优化问题求解的元启发式算法
2.3.3、路径优化问题求解算法的改进.
2.4、文献评述.
第3章 Y企业生鲜农产品配送路径优化模型构建
3.1、Y企业主营业务与存在问题分析
3.1.1、企业现状概述.
3.12、企业主营业务与流程.
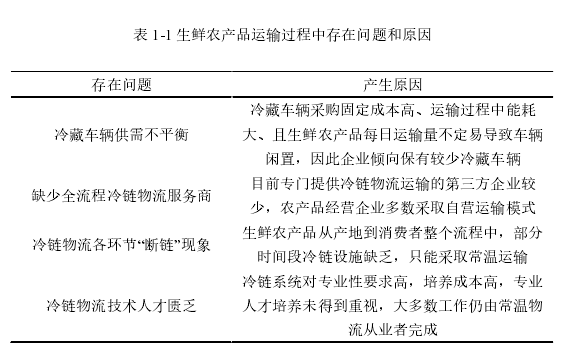
3.13、配送过程存在的问题.
3.2、模型基本假设与符号说明
3.2.1、模型描述与基本假.
3.2.2、参数与符号说明
3.3、配送车辆路径优化模型目标函数的构建
3.3.1、配送的运输成本.
3.3.2、生鲜农产品货损成本.
3.3.3、时间窗惩罚成本.
3.4、配送车辆路径优化模型的构建.
3.5、本章小结.
第4章 模型求解算法设计与 改进.
4.1、遗传算法基本原理.
4.2、人工蜂群算法基本原理.
4.3、遗传-人工蜂群算法设计
4.3.1、构造初始可行解.
4.3.2、邻域搜索方法.
4.3.3、食物源评价策略.
4.3.4、遗传算子改进人工蜂群算法.
4.4、整体算法流.
4.5、本章小结.
第5章 Y 企业配送路径优化算例分析
5.1、算例背景概述.
5.2、算例模型求解.
5.2.1、算例模型参数设定.
5.2.2、算例结果分析.
5.2.3、算法求解结果对比.
5.3、灵敏度分析
5.3.1、门店需求量灵敏度分析
5.3.2、车辆行驶速度灵敏度分
5.3.3、农产品服务系数灵敏度分析
5.4、本章
第6章 结论
本文所获得的主要结论如下:
(1)通过梳理Y连锁超市的主营业务和流程并结合所运输生鲜农产品的特点,总结出Y连锁超市企业目前直营配送方式存在的主要问题:配送路线经验性选择较强、对门店期待送达时间不够重视、配送方案预案不足和对货损成本重视不够。
(2)在Y企业生鲜农产品配送的建模过程中,本文根据企业目前存在的问题建立了相应的路径优化模型,并分别对目标函数的各个部分含义与设定依据进行了阐述,其中将货损函数分为运输货损和卸货服务货损,分别使用负指数分布形式来描述生鲜农产品质量下降所带来的成本,同时根据各个客户点的期望到达时间和要求到达时间设定了软硬时间窗约束,使模型更能反映Y企业生鲜农产品配送的实际情况。针对模型求解的元启发式算法,本文选择遗传算法和人工蜂群算法,并采用一种遗传思路改进的人工蜂群算法对该路径优化模型进行求解。
(3)在Y企业生鲜农产品配送的算例中,首先通过算法求解结果对比证明遗传-人工蜂群算法在求解模型时可以有效提高人工蜂群算法的全局搜索能力,相比于改进前效果有较大提升,能获得更好的求解结果。其次通过对案例的求解和对客户需求量、车辆行驶速度和农产品服务系数的灵敏度分析,本文得到的结论包括:门店需求量变动主要影响货损成本,因此可以在门店举办促销活动需求量突然增加的情况之前,通过临时租用更高质量的冷链车辆降低运输货损成本,或临时雇用熟练卸货工人降低服务货损成本;车辆行驶速度变动的主要影响在时间窗成本,若车辆行驶速度具有周期规律,则可以与某些门店进行协商,更改门店的期望到达时间,进而降低时间窗成本;农产品服务系数变动的影响主要体现在卸货服务成本,提高企业在卸货服务过程中的农产品服务系数,对降低配送成本作用巨大,因此建议门店对卸货操作工人进行系统化培训以降低农产品服务系数。
参考文献
[1]交通运输部.交通运输部关于加快发展冷链物流保障食品安全促进消费升级的施意见[EB/OL].2017- 8-22.
[2]国务院办公厅.国务院办公厅关于加快发展冷链物流保障食品安全侃进消费升级的意见[EB/OL]. 20174-13. -04/21/content_ _51 8796 l .htm
[3]中华人民共和国国家标准一_物流 术语[J].交通建设与管理,2007( 10): 106-120.
[4]ClarkSD,周水洪,欧阳军.易腐食品冷链百科全书[M].东华大学出版社,2009.
[5] Abad P L, Aggarwal V. Incorporating transport cost in the lot size and pricingdeci si ons with downward sloping dem and[J]. International Journal of ProductionEconomics, 2005, 95(3): 297 -305.
[6] KuoJ C, Chen M C. Developi ng an advanced mu lti-temperature joi nt distributionsy stem for the food cold chai n[J]. Food control, 2010, 21(4): 559-566.
[7] Van Duin J H R, De Goffau W, Wiegmans B, et al. Improving home deliveryefficiency by using princi ples of address inteligence for B2C deliveri es[J].Transportati on Research Procedia, 2016, 12: 14-25.
[8]廖佑莲,谢明冷链物流一体化发展趋势研究[J].中国物流与采购,2020(23):101-102.
[9] Dantzig G B, Ramser J H. The truck dispatchi ng problem[J]. Management science,1959, 6(): 80-91.
[10]Wang Z, Li Y, Hu X. A heuristic approach and a tabu search for the heterogeneousmulti type fleet vehic le routi ng problem with time windows and an incompatibleloadi ng constraint[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2015, 89: 162-176.
[11]Deng Y, Zhu W, Li H, et al. Multi -type ant system algorithm for the time dependentvehicle routing problem with time windows[]. Journal of Systems Engineeri ngand Electronics, 201 8, 29(3): 625-638.
[12].王旭坪,阮俊虎,孙自来,曹海艳.带回程取货车辆路径问题的干扰恢复模型[J].系统工程学报,2013,28(05 ):608-616.
[13]Liu R, Xie X, Augusto V, et al. Heuristic algorithms for a vehicle routi ng problemwi th simultaneous delivery and pickup and time windows in home health care[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 2013, 230(3): 475 -486.
[14]易云飞,蔡永乐,董文永,林晓东.求解带用户满意度的多目标实时车辆路径问题的改进伊藤算法[J].电子学报,2015 ,43(10):2053-2061.
[15]张瑾,毕国通,戴二壮.双目标冷链物流车辆路径问题及其遗传蚁群求解[J].科学技术与工程,2020,20( I 8):74 13-7421.
[16]李桃迎,吕晓宁,李峰,陈燕.考虑动态需求的外卖配送路径优化模型及算法[J].控制与决策,2019,34(02):406-413.
[17]Solomon M M. Algorithms for the vehicle routing and schedu ling problems withtime window constraints[J]. Operations research, 1987, 35(2): 254-265.
[18]Savelsbergh M. Local search for routing problem with time windows[ R]. Annalsof Operations Research, 1985, 164(4 ): 285 -305.
[19]邵可南,吕成瑶张帅师帅,宫婧.一种基于冷链低碳物流路径的混合优化算法[].计算机技术与发展,2021,31(02):27-32.
[20]侯玉梅,贾震环,田歆,尉芳芳.带软时间窗整车物流配送路径优化研究[]系统工程学报,2015,30(02):240-250.
[21]CaoQ K, Yang K W, Ren X Y. Vehicle routi ng optimizati on with muli ple fuzzytime windows based on improved wolf pack algorithm[J]. Advances in ProductionEngineering & M anagement, 2017, 12(4): 401411.
[22]葛显龙,竹自强.带软时间窗的电动车辆路径优化问题[].工业工程与管理,201 9,24(04):96-104+112.
[23]李珍萍,张煜炜.带时间窗和服务顺序约束的多需求车辆路径问题[J].控制与决策201 9,34(07):1565-1570.
[24]周鲜成,王莉,周开军,黄兴斌.动态车辆路径问题的研究进展及发展趋势[J].控制与决策,2019,34(03):449-458.
[25]Osvald A, Stirn L Z. A vehicle routing algorithm for the di stribution of freshvegetables and similar peri shable food[J]. Journal of food engi neeri ng.2008, 85(2):285-295.
[26] Gong W, Fu Z. ABC-ACO for peri shable food vehic le routing problem with timewi nd ows[C ]/2010 international conference on computational and informationsciences. IEEE, 2010: 1261-1264.
[27]Mahmudy W F Improved simu lated annealing for optimizati on of vehicle routingproblem wi th time windows (VRPTW)[J]. Jurnal Ilmiah Kursor, 2014, 7(3).
[28]Hsu C I, Hung S F, Li H C. Vehicle routing problem with time-windows forperishable food delivery[J]. Journal of Food Engi neering, 2007, 80(2):465-475.
[29]曹倩,邵举平,孙延安基于改进遗传算法的生鲜农产品多目标配送路径优化[J].工业工程,2015,18(01):71-76.
[30]冀巨海,张璇.考虑取送作业的生鲜农产品配送路径优化模型与算法[J].系统科学学报2019,27(01):130-135.
[31]宋志兰,黄欢,张壮时间窗约束下带逆向物流的冷链物流车辆路径优化研究[J].
生鲜农产品具有不同于其他产品的特点,例如易腐烂、不易储存等,因此生鲜农产品的物流配送就具有一些特殊性,它关系到不同位置的生鲜农产品是否能实现保证质量前提下的有效互通和共享。...