摘要: 以 2 种内镶片式迷宫流道滴头为研究对象,采用数学分析方法、扫描电镜/能谱分析技术( SEM-EDS) 和X 射线衍射技术( XRD) 对不同水溶性肥料滴灌后滴头流量、堵塞物表面微形貌及其化学组分进行多角度分析,研究肥料特性和流道结构对滴头堵塞过程的影响效应。结果表明: 肥料特性是决定堵塞类型和诱发风险的重要因素( P <0. 01) ,流道结构对堵塞的影响需双重考虑结构尺寸及结构类型; 当施肥质量分数小于等于 0. 5% 时,施肥加速滴头堵塞的效果较小且与肥料类型关系不大,当施肥质量分数在 0. 5% ~2. 0% 之间时,各肥料滴灌适用性由大到小依次为: 磷肥、尿素、钾肥、复合肥,当施肥质量分数在 2. 0% ~ 3. 0% 之间时,尿素滴灌滴头流量降幅为10. 26% ,显着高于施加磷肥( 7. 85% ) 、钾肥( 4. 07% ) 和复合肥( 2. 74% ) ; 施加尿素滴灌诱发滴头堵塞主要物质的形成机理为分子态尿素析出物与水中悬浮颗粒物形成团聚体在较差流体的运动粘度下造成的物理堵塞,磷肥主要为吸附作用加速肥料杂质团聚沉淀的物理、化学堵塞,硫酸钾施肥滴灌主要为离子交换形成的钙、镁沉淀导致流道壁面糙度升高、过水断面减小的化学堵塞过程,复合肥诱发滴头堵塞风险最低。施肥滴灌存在诱发或者加速滴头堵塞的风险,但不同肥料诱发滴头堵塞主要物质的形成机理不同,加速堵塞的风险也不同,故对于不同的肥料类型宜采用不同的抗堵塞管理策略。
关键词: 滴灌施肥; 滴头; 堵塞; 风险; 机理。
Abstract: The inducing mechanism of emitters clogging with fertigation was explored. A laboratoryexperiment was conducted to investigate the influence of three factors ( fertilizer types, fertilizerconcentration and flow path structure) on anti-clogging performance of drip emitters. The intermittent dripirrigation experiment was studied by using two flow path types of non-pressure compensating emitters( arc-shaped saw-tooth and cup-shaped saw-tooth) ,four levels of fertilization concentration ( 0. 5%,1. 0% ,2. 0% and 3. 0% ) and four types of fertilizer ( urea,calcium superphosphate,potassium sulfateand water soluble compound fertilizer) and the system was allowed to run for 20 h. The mathematicalanalysis methods in combination with field scanning electron microscope ( FESM) ,energy dispersivespectrometer ( EDS ) and X-ray diffraction ( XRD ) technology were then used to quantitatively andqualitatively analyze the variations of the emitter's average relative flow rate,surface topographicalcharacteristics and components of the clogging materials internal emitters. Results showed that fertilizercharacteristic was an important factor in deciding the emitter clogging type and degree ( P < 0. 01) ,andthe influence of the two flow path structures on the accelerating effect of emitter clogging performanceneeded to consider the path structural size and style. The accelerating effect of fertilizer application onemitter was not obvious when the concentration of fertilizer solution was less than 0. 5% . When theconcentration was increased to 0. 5% ~ 2. 0% ,there were obvious changes in the quantities of outflowdischarge occurred in phosphate-fertigation,which made it clog easily,followed with urea-fertigation,theapplicability of potassium-fertigation and compound-fertigation was better than that of the former. Whenthe concentration was risen to 2. 0% ~ 3. 0% or higher,the clogging degree was so serious with urea-fertigation,the flow rate was decreased by 10. 26% ,which was significantly higher than those ofphosphate-fertigation ( 7. 85% ) ,potassium-fertigation ( 4. 07% ) and compound-fertigation ( 2. 74% ) .Fertilization can promote the clogging of the emitters. These fertilizer types had different water quality,hence resulting into different emitter clogging risk and inducing mechanism. Emitters clogging with ureafertigation were caused by the role of aggregation and adhesion with both crystallization of the molecularurea state and suspended particles in the water. The adsorption function that particulate impurities tophosphorus promoted flocculation while precipitation among solid particles was as a result of inducingmechanism of emitter clogging with phosphate fertigation. The main inducing mechanism for emitterclogging with potassium-fertigation was chemical precipitation because of the ion-exchange action,whileemitter clogging with compound-fertigation had the lowest risk. Therefore,fertigation with differentfertilizer types should adopt different emitter clogging controlling management strategy.
Key words: fertigation; emitter; clogging; risk; mechanism.
引言。
滴灌施肥是定量供给作物水分和养分并维持土壤适宜水肥浓度的有效方法,其精量性可改善旱地农业水肥资源利用现状、缓解水资源危机、促进作物生长[1],也是旱地农业技术未来发展的研究重点。水中大量矿物微粒、肥料离子和细小固体悬浮颗粒大大提高了滴头堵塞风险,而滴头堵塞又直接决定了滴灌系统的使用寿命及经济效益[2 -3].已有研究表明,水体中高浓度的 Ca2 +、Mg2 +、HCO3 -、SO2 -4等无机离子组分以及相对较高的 pH 值,是造成滴头流道淤积的重要因素[4].然而,施肥滴灌改变水源中营养物质的种类、浓度、水中悬浮颗粒数量、水温、pH 值、电导率等参数,导致各类溶质在流道内水流紊动作用下相互碰撞、吸附、团聚、沉淀形成的堵塞淤积规律改变,由此诱发堵塞风险更高,堵塞机制更为复杂且与施肥浓度呈正相关[5 -13],滴头有效率仅为50% ~75%[14].其中,小流量滴头高浓度施肥条件滴头堵塞程度最高,且含有 P、Ca、Mg、Fe、S 的肥料类型可显着提高诱发滴头堵塞的风险[15 -16].因此,研究施肥滴灌过程中,滴头堵塞过程及形成机理对于防治水肥一体化过程中滴头堵塞,提高滴灌系统运行效率具有重要意义。但以往研究仅针对单一流道结构,或者单一肥料类型,在不同肥料类型和浓度条件下对于不同结构形式流道加速滴头堵塞的风险是否一致,诱发堵塞的机理是否相同,这些问题都还有待于进一步研究和确认。
本文选用 2 种结构形式流道滴头,在 4 种不同肥料类型及 4 种肥料浓度梯度条件下,在对施肥滴灌滴头流量变化过程测试基础上,讨论施肥滴灌滴头堵塞的发生规律,并借助装有能谱仪( EDS) 的场发射扫描电镜( FESEM,S-4800 型,日立) 对堵塞物质表面形貌进行显微分析和元素分析,同时配合采用 X 射线衍射仪( XRD,D8 Adance,Bruker) 确定不同肥料类型滴灌诱发滴头堵塞主要物质的化学组分,揭示滴头堵塞的诱发机制,评估和预测滴头堵塞风险,旨在为水肥滴灌影响下合理防治滴头堵塞管理策略提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法。
1. 1 试验材料制备。
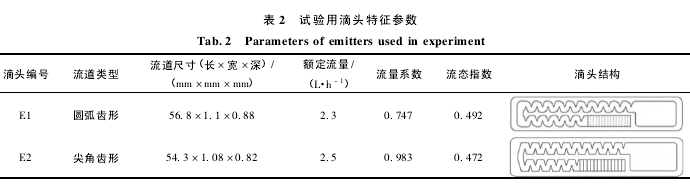
试验用水为陕西杨凌示范区居民自来水,通过环境保护局 2015-2016 年最新监测数据来看,符合我国农田灌溉用水水质标准[17]( 表 1) ,细菌数小于1 CFU / mL,短周期滴灌可忽略生物堵塞的影响,故该水质条件下研究水肥特性对滴头堵塞影响的试验结果具有一定的代表性。试验选用滴头参数如表 2所示。
试验选用 4 种可溶性肥料,分别为氮肥、磷肥、钾肥和复合肥。氮肥为尿素( 云南三环化工股份有限公司) ,分子式 CO( NH2)2,粒径 1 ~2 mm 的半透明粒子。尿素极易溶于水且无任何杂质,溶液呈透明状。试验用磷肥为过磷酸钙( 河北省矾山磷矿有限公 司) ,含 磷 组 分 为 磷 酸 二 氢 钙 的 水 合 物Ca( H2PO4)2·H2O,杂质为硫酸钙、二氧化硅和少量游离的磷酸和硫酸,常温下是灰白色粉末。过磷酸钙含有效 P2O5质量分数 14% ~ 20% ( 其中80% ~95% 溶于水) ,属于水溶性速效磷肥。制备磷肥水溶液时,搅拌后溶液浑浊,溶液底部存在大量灰色粉末状沉淀,待过磷酸钙颗粒在玻璃烧杯中充分溶解、静置后,取上清液透明液体,经浓度检测后作为试验材料。试验用钾肥为硫酸钾( 山东鲁丰钾肥有限公司) ,硫酸钾含 K2O 质量分数 50% ~ 54% ,淡灰色微晶体粉末状。制备硫酸钾溶液过程中,经充分搅拌溶解后溶液底层沉积灰白色沉淀同时肥液表层悬浮白色包膜材料,待静置分层经过滤后取上清液,经浓度检测后作试验材料。复合肥采用临沂沃夫特复合肥有限公司生产的全水溶高钾型螯合态化肥,主要成分为尿素、磷酸二氢钾、硝酸钾,其中氮、磷和钾质量比为 16∶ 6∶ 28.该肥料极易溶于水,溶液呈淡蓝色透明状。