摘 要: 目的了解广西多民族大学生肺活量和体成分的基本情况, 并探讨两者的相关性。方法对自愿参加调查的广西某高校1322名学生进行肺活量及体成分测定, 并进行统计学分析。结果汉族、壮族及其他少数民族大学生的肺活量、肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分及蛋白质均存在民族差异 (P<0.05) ;相关分析中, 肺活量与脂肪量成负相关关系 (相关系数r=-0.092, P<0.01) ;肺活量与肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分及蛋白质含量成正相关关系 (相关系数分别为0.687、0.633、0.658及0.653, 均P<0.01) 。结论广西多民族大学生的肺活量及部分体成分存在民族差异, 三者中肺活量及部分体成分的比较:汉族>其他少数民族>壮族;增加肺活量, 则体内脂肪量越低, 肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分及蛋白质含量越高。
关键词: 多民族; 肺活量; 体成分分析; 大学生;
Abstract: Objective To study the basic situation of vital capacity and body composition of the multi ethnicity college students in Guangxi, and to explore the correlation between vital capacity and body composition.MethodsThe vital capacity and body composition of 1322 students who volunteered to participate in the investigation in a college in Guangxi were measured, and carried on the statistical analysis.ResultsThere were ethnic differences in vital capacity, muscle volume, estimated bonse mass, body moisture and protein among the Han, Zhuang and other ethnic minority students (P<0.05) .In the correlation analysis, the vital capacity and the amount of fat were negatively correlated (correlation coefficient r=-0.092, P<0.01) .The vital capacity and muscle mass, the presumption of bone mass, body moisture and protein content were positively correlated (correlation coefficients were 0.687, 0.633, 0.658, 0.653, respectively and P<0.01) .Conclusion Ethnic differences are in vital capacity and some body composition among ethnic university students in Guangxi, and the comparison of the vital capacity and body composition among the three are:Han>Other minorities>Zhuang.The higher lung capacity, the lower the amount of fat in the body, and the higher muscle mass, bone mass, body moisture and protein content.
Keyword: Multi ethnicity; Vital capacity; Body composition analysis; College student;
研究表明, 近三十年来, 我国大学生的体质呈下降趋势[1,2,3]。随着我国社会经济的发展, 虽然大学生的体质量、身高等形态学指标呈现上升趋势, 但心肺功能、速度耐力、肌肉爆发力等综合素质却呈下降趋势[4]。这一状况已引起社会的广泛关注。肺活量与身高、体重、胸围等密切相关, 已作为人体生长发育水平的功能指标之一[5]。体成分包括体内脂肪量、水分含量、推测骨量及蛋白质含量等, 是衡量体质健康的重要指标, 其质量及分布与各年龄阶段人群的健康状况密切相关[6,7]。目前, 国内外有关肺活量与身体质量指数 (body mass index, BMI) 、体脂率及腰臀比等的相关研究报道较多[8,9,10], 但关于现有资料中鲜见肺活量与体成分相关性的报道。因此, 本研究主体为受疾病干扰较少的广西多民族大学生群体, 通过测量肺活量和体成分, 并探讨肺活量与体成分的相关关系, 为进一步提高大学生体质健康提供一定的科学理论依据。
一、对象和方法
1.研究对象
选取广西某高校1322名自愿参加测试的大学生, 其中汉族大学生873名, 壮族大学生331名, 其他少数民族 (包括瑶族、苗族、侗族、土家族、布依族等少数民族) 118名, 平均年龄分别为 (20.47±1.41) 岁、 (20.49±1.38) 岁及 (20.72±1.63) 岁, BMI分别为19.59±2.16、19.41±2.19及19.76±2.31, 3组大学生的年龄及BMI均无民族差异。参与测试的志愿者身体正常, 无外伤、高血压、糖尿病、甲状腺疾病等, 且近半年无服用钙剂、类固醇激素等。所有测试者均自愿参与, 并签署知情同意书。
2.方法
2.1肺活量的测量:采用肺活量测试仪测量志愿者的肺活量, 每个志愿者测量3次, 取均值。测定由经过专业培训的人员进行。

2.2体成分的测量:采用百斯人体成分分析仪 (Bio-space In Body 3.0) 测量体成分, 测量指标包括体重、BMI、脂肪量、肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分、蛋白质等。测试时, 志愿者需裸脚进行测量, 并由经过专门培训的人员指导和操作。身高使用身高计测试, 准确到0.1 cm。
3.数据分析
采用SPSS 16.0统计学软件进行数据分析, 结果用均值±标准差 (±s) 表示, 组间差异采用方差分析;肺活量与体成分的相关性分析采用Pearson线性分析。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
二、结果
1.广西多民族大学生的肺活量及体成分
如表1所示, 汉族、壮族及其他少数民族大学生的肺活量、肺活量分数存在民族差异 (均P<0.01) , 3组肺活量大小的比较:汉族>其他少数民族>壮族;汉族、壮族及其他少数民族大学生的脂肪量差异无统计学意义 (P>0.05) , 肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分、蛋白质均存在民族差异 (P值分别为0.003、0.002、0.021、0.000) , 3组体成分相比:汉族>其他少数民族>壮族。
2.肺活量与体成分的相关性分析
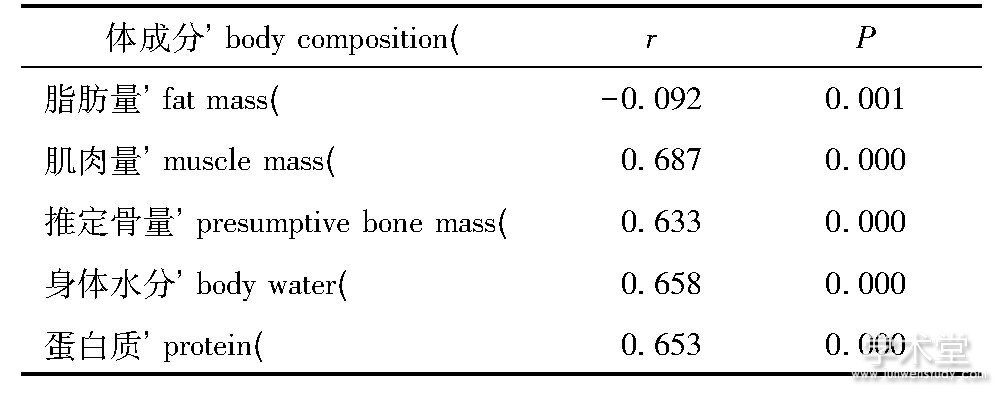
如表2所示, 肺活量与脂肪量成负相关关系 (相关系数r=-0.092, P<0.01) , 与肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分及蛋白质成正相关关系 (相关系数分别为0.687、0.633、0.658、0.653, 均P<0.01) 。
3.肺活量与体成分相关关系散点图
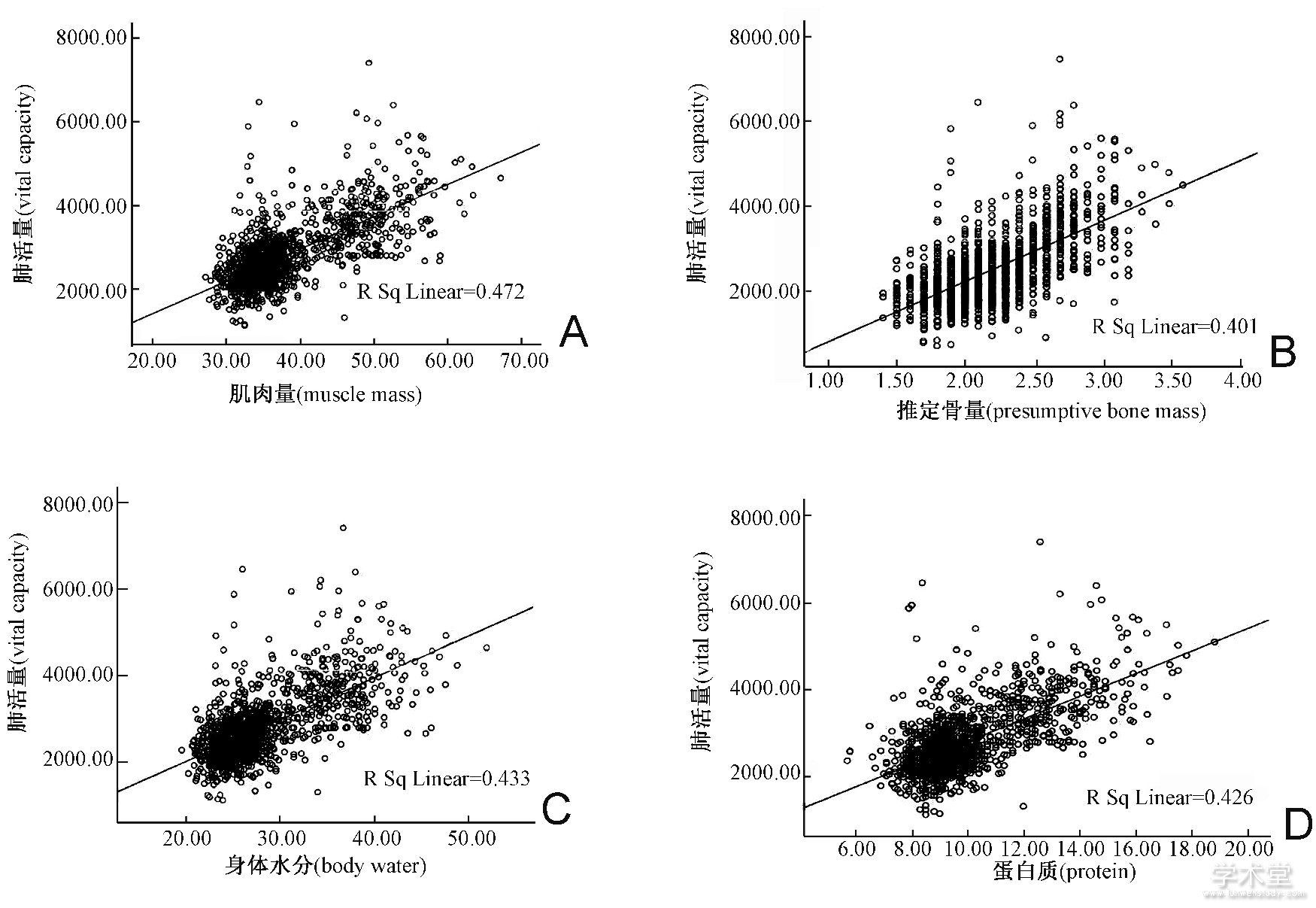
如图1所示, 随着肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分及蛋白质的增加, 肺活量均呈上升趋势 (相关系数分别为0.687、0.633、0.658及0.653, 均P<0.01) 。
表1 广西多民族大学生体成分及肺活量Table 1 Body composition and vital capacity of Guangxi multi ethnicity university students
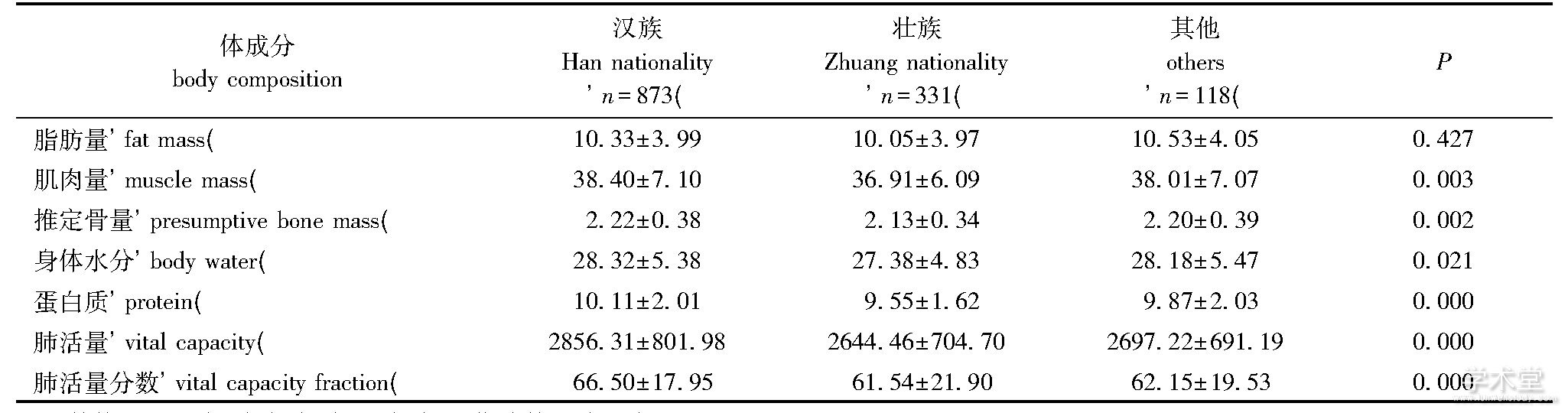
其他包括瑶族、苗族、侗族、土家族、布依族等少数民族Others include Yao, Miao, Dong, Tujia, Buyi and other ethnic minorities
表2 肺活量与体成分的相关关系Table 2 Correlation between vital capacity and body composition
三、讨论
相关调查和研究表明, 目前我国大学生由于对自身健康状况缺乏正确的认识, 导致缺乏有效的体育锻炼[11]。尤其是近些年来, 大学生体质下降的趋势越来越显着, 已引起社会广泛的关注。有研究指出, 大学生课业负担重而且日常锻炼不足, 是大学生体质下降的主要原因[12]。本次的研究对象是在校大学生, 除了日常的学习压力以外, 不良的生活方式也是影响体质状况的重要原因之一[13,14], 主要表现为:不吃早餐、熬夜、生活不规律等。此外, 在校大学生普遍对体育锻炼缺乏重视, 较少参与运动和锻炼。
图1 肺活量与体成分相关关系散点图Fig.1 Scatter diagram of correlation between vital capacity and body composition
本次研究发现, 3组在校大学生的肺活量及体成分 (肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分、蛋白质) 含量的比较中:汉族>其他少数民族>壮族, 即汉族大学生的肺功能及体成分 (肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分及蛋白质) 要优于壮族和其他民族, 出现这种状况的原因:首先, 可能是汉族、壮族及其他少数民族在遗传素质方面的差异, 导致了肺活量及体成分的不一致[15,16,17];其次, 可能与饮食习惯有一定关系[18]。广西的壮族和其他少数民族世代居住在山区为主, 因为山区的生产生活条件所限, 他们的饮食主要以素淡之物为主, 尤其喜食玉米;另外, 不同民族居住的环境也会对人体体质状况造成不同影响[19,20]。
肌肉和脂肪是构成人体的重要组织, 脂肪含量和肌肉量的多少也与体质健康有很大关系[21]。本研究结果发现, 肺活量与肌肉量成正相关, 同脂肪量成负相关关系, 这与聂环玲等[22]的研究结果相似, 均说明脂肪量和肌肉量同人体的肺通气功能存在相关性。原因可能是当体脂含量减少时肌肉量会相应增多, 而脂肪量减少时则会使肺活量增高[23]。因此, 当机体脂肪量减少、肌肉量增多时可以改善肺功能。
骨量是指是单位体积内骨组织的含量, 该参数是衡量骨骼健康情况的重要指标之一。目前有研究发现, 肌肉量[24]和负重运动[25]是影响骨密度的重要因素。本研究结果显示, 随着推定骨量的增加, 肺活量也呈上升趋势。原因可能由于体育锻炼不仅可以增加肌肉量[26]和骨量, 还可以明显增加呼吸肌的力量, 提高肺的功能, 使呼吸的深度加大、加深, 从而增加肺活量。
细胞内外液、体脂肪、蛋白质等人体成分是维持机体正常结构和功能的物质基础, 这些物质的主要成分是水, 其均衡状态对维持机体内环境的稳定有着重要作用, 是影响人体健康的重要因素[27]。曹兵等[28]研究发现, 长期坚持锻炼可以显着增加机体的水分和蛋白质, 同时又能明显改善呼吸功能。本研究发现, 肺活量同身体水分和蛋白质成正相关, 与曹兵等的研究结果一致。
通过本研究表明, 广西少数民族大学生肺活量和体成分 (肌肉量、推定骨量、身体水分、蛋白质) 含量均低于汉族大学生, 少数民族学生的体质状况有待改善, 需要引起社会的关注。
参考文献:
[1]Zhang B, Yu X.Investigation and research on college students'physical health[J].Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2015, 12 (4) :51. (in Chinese) 张斌, 于秀.大学生体质健康现状调查与研究[J].科技创新导报, 2015, 12 (4) :51.
[2]Wen XT.Analysis of influencing factors of college students'physical health decline[J].Science and Technology Vision, 2016, (2) :128. (in Chinese) 闻先涛.大学生体质健康下降的影响因素分析[J].科技视界, 2016, (2) :128.
[3]Yu T.Analysis of physical health status of college students in Tianjin[J].Chinese Journal of School Health, 2010, 31 (8) :976-978. (in Chinese) 于涛.天津市大学生体质健康状况分析[J].中国学校卫生, 2010, 31 (8) :976-978.
[4]Fang F.Self intervention of adolescent health promotion under the background of college students'physical decline[J].Journal of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 31 (5) :968-969. (in Chinese) 方放.大学生体质下降背景下青少年健康促进的自我干预[J].长春中医药大学学报, 2015, 31 (5) :968-969.
[5]Wei LCh, Pan Y.Body mass index (BMI) and vital capacity weight index of Baise health school students[J].Applied Preventive Medicine, 2015, 21 (3) :192-193. (in Chinese) 韦柳春, 潘毅.百色卫校中职生体质指数 (BMI) 与肺活量体重指数[J].应用预防医学, 2015, 21 (3) :192-193.
[6] Chomtho S, Fewtrell MS, Jaffe A, et al.Evaluation of arm anthropometry for assessing pediatric body composition:evidence from healthy and sick children[J].Pediatr Res, 2006, 59 (6) :855-860.
[7]Bai JY, He Y, Hai XJ, et al.Changes in bone mineral density and body composition of Hui college students[J].Acta Anatomica Sinica, 2015, 46 (3) :410-414. (in Chinese) 白静雅, 何烨, 海向军, 等.回族大学生骨密度和体成分的变化特点[J].解剖学报, 2015, 46 (3) :410-414.
[8]Wang X, Deng XW.Relationship between body fat content and pulmonary ventilation function and metabolic indexes in adult males[J].Medical Journal of the Chinese People Armed Police Forces, 2014, 25 (9) :872-874. (in Chinese) 王翔, 邓笑伟.成年男性身体脂肪含量与肺通气功能及代谢指标的关系[J].武警医学, 2014, 25 (9) :872-874.
[9]Zhang YK, Ma DD, Xiao W, et al.Effects of body composition on pulmonary ventilation function in normal adult women in Ji'nan[J].Journal of Shandong University (Medical Edition) , 2011, 49 (8) :113-117. (in Chinese) 张玉可, 马德东, 肖伟, 等.济南地区普通成年女性体成分对肺通气功能的影响[J].山东大学学报 (医学版) , 2011, 49 (8) :113-117.
[10] Fukahori S, Matsuse H, Takamura N, et al.Body mass in dex correlated with forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity in a population with a relatively low prevalence of obesity[J].Chin Med J, 2010, 123 (20) :2792-2796.
[11]Sun RH.Analysis of the causes of college students'physical quality decline from the perspective of nutrition and exercise---Taking students of China Jiliang University as an example[J].Sports Science and Technology, 2015, 36 (3) :36-38. (in Chinese) 孙若海.从营养学与锻炼学视角分析大学生身体素质下降成因---以中国计量学院学生为例[J].体育科技, 2015, 36 (3) :36-38.
[12]Luo ChW.Research on college students'sports behavior and physique from the perspective of environment[J].Contemporary Sports Science and Technology, 2014, 4 (32) :186, 188. (in Chinese) 罗畅伟.环境视角下大学生体育行为与体质问题研究[J].当代体育科技, 2014, 4 (32) :186, 188.
[13]Luo LN, Su WT, Yang ST.The influence of unhealthy habits on college students'physical fitness[J].Contemporary Sports Science and Technology, 2017, 7 (20) :18. (in Chinese) 罗丽娜, 苏文涛, 杨思瞳.不良生活习惯对大学生体质健康的影响[J].当代体育科技, 2017, 7 (20) :18.
[14] Xie L.Study on the relationship between college students'lifestyle and physical health---taking Hunan Institute of Humanities Science and Technology as an example[J].Sports Excellence (Academic Edition) , 2015, 34 (11) :87-89. (in Chinese) 谢利.大学生生活方式现状及其与体质健康的关系研究---以湖南人文科技学院为例[J].运动精品 (学术版) , 2015, 34 (11) :87-89.
[15]Pan XY.Regional characteristics of vital capacity in Chinese minority children and adolescents[J].Modern Preventive Medicine, 2016, 43 (5) :824-826, 863. (in Chinese) 潘锡炎.中国少数民族儿童青少年肺活量发育水平的地域特征分析[J].现代预防医学, 2016, 43 (5) :824-826, 863.
[16]Cao Y, Li YL, Lu Sh H, et al.Comparison of body composition and body mass index between Han and Mongolian college students[J].Journal of Tianjin Normal University (Natural Edition) , 2011, 31 (2) :69-72. (in Chinese) 曹瑜, 李玉玲, 陆舜华, 等.汉族、蒙古族大学生体成分与体质指数的比较[J].天津师范大学学报 (自然版) , 2011, 31 (2) :69-72.
[17]Zhang ShL, Li XT, Lei H, et al.Comparative analysis of physical fitness of Han and Mongolian college students[J].Sichuan Physical Education Science, 2012, (5) :76-80. (in Chinese) 张胜林, 李小唐, 雷慧, 等.汉、蒙古族大学生体质健康状况比较分析[J].四川体育科学, 2012, (5) :76-80.
[18]Zhang M, Wang Zh F.Investigation and analysis of nutrition knowledge, attitude and dietary behavior among college students of different nationalities[J].Health Vocational Education, 2012, 30 (4) :125-126. (in Chinese) 张明, 王志凡.不同民族大学生营养知识、态度及饮食行为调查分析[J].卫生职业教育, 2012, 30 (4) :125-126.
[19]Su L, Wei LQ, Qu JT, et al.Comparative analysis of adult physical condition in different economic development areas in Henan[J].Sports Science and Technology Literature Bulletin, 2012, 20 (7) :88-91. (in Chinese) 苏丽, 魏柳青, 屈金亭, 等.河南省不同经济发展地区成年人体质状况的比较分析[J].体育科技文献通报, 2012, 20 (7) :88-91.
[20]Chen Y.Physical and nutritional status of primary and middle school students in different regions of Chongqing[D].Third Military Medical University, 2013. (in Chinese) 陈燕.重庆市不同地区中小学学生体质与营养状况调查[D].第三军医大学, 2013.
[21]Hou XL, Shi Zh.Correlation between body composition and physical fitness indicators of college students[J].Business, 2014, (1) :352. (in Chinese) 侯新亮, 史振.高校学生身体成分与体质健康指标的相关性研究[J].商, 2014, (1) :352.
[22]Nie HL, Zhang XW, Wang K.Correlation between body composition and cardiorespiratory function[J].Chinese Journal of School Doctor, 2011, 25 (9) :655-656. (in Chinese) 聂环玲, 张晓伟, 王科.身体成分与心肺功能的相关性研究[J].中国校医, 2011, 25 (9) :655-656.
[23] Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Whincup PH.Body fat distribution, body com-position, and respiratory function in elderly men[J].Am J Clin Nutr, 2005, 82 (5) :996-1003.
[24]Yang XL, He Y, Ma LY, et al.Correlation between body composition and bone mass abnormality in Tibet Tibetan[J].Acta Anatomica Sinica, 2017, 48 (2) :199-203. (in Chinese) 杨秀琳, 何烨, 马力扬, 等.西藏藏族成人体成分与骨量异常的相关性[J].解剖学报, 2017, 48 (2) :199-203.
[25]Ceng YW, Sun Zh Q.Analysis of correlation between exercise and bone mineral density[J].Biotechnology World, 2015, (10) :247-248. (in Chinese) 曾裕文, 孙正启.运动与骨密度变化相关性分析[J].生物技术世界, 2015, (10) :247-248.
[26]Lu JY, Zhang H.Effect of aerobic exercise on physical fitness of college students under the guidance of exercise prescription[J].Hubei Sports Science and Technology, 2017, 36 (2) :168-172. (in Chinese) 路金豫, 张慧.运动处方指导下有氧运动对大学生体质影响[J].湖北体育科技, 2017, 36 (2) :168-172.
[27]Chen LM, Fu YL, Li HJ, et al.Correlation between constitution of Chinese medicine and body composition[J].Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 32 (3) :1242-1245. (in Chinese) 陈丽名, 傅延龄, 李洪娟, 等.中医体质与人体成分的相关性研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32 (3) :1242-1245.
[28]Cao B, Shi F.Analysis of physical and body composition characteristics of long term adherence to exercise for elderly men[J].Sports, 2017, (1) :155-156. (in Chinese) 曹兵, 石峰.长期坚持八段锦锻炼的老年男性体质和身体成分特征分析[J].运动, 2017, (1) :155-156.
我国是个多民族国家,区域和种族之间风俗和生活习惯的差异,使不同地理区域的居民呈现出不同的体质特征。我国少数民族青少年体表面积的研究已见一些报道[1-2],但对体表面积的多元分析鲜有研究。人体体表面积不仅与人的基础代谢、肺活量、心输出量、肾小球过...