摘 要: 城市化对水系演化影响的研究国内目前多集中在快速、高速城市化地区,而对大流域、城市化发展较缓地区的研究比较薄弱。 以南四湖流域为研究区,基于 1987、2000 和 2014 年 3 期遥感影像,分析了流域城市化进程中的下垫面变化特征; 选取流域 1980s、2003 和 2014 年的地形图进行水系提取,从数量参数、结构参数和连通性参数 3 个角度分析近30 年城市化进程中水系结构的时空变化特征。 结果表明: ( 1) 近 30 年来流域建设用地增加了 1568.06 km2,2000 年以后城市建设用地扩张显着,2012 年流域人口城市化率为 32%; ( 2) 1980s 2010s 流域总河流长度、面积和河网密度均呈现出持续减少趋势,分别减少了 135.46 km、2.75 km2和 0.49 km/km2,各级河流表现出不同的变化特点,较低等级河流受到的影响较大; 而流域水面率持续增加,近 30 年共增加了 59.79%; ( 3) 流域水系总体上还保持着自然状态下的空间格局,但结构特征发生了较大改变,河网结构稳定度减少了 4.30%,连接率和实际结合度分别减少了 21.82%和 21.62%; 子流域内部距湖区越远的空间城市扩展强度指数值越大,城市化对水系的影响越显着。 该研究将补充对不同空间尺度、不同城市化水平地区河网水系演化影响的案例,并为研究区河网水系的保护提供支持与参考。
关键词: 城市化; 水系结构; 下垫面变化; 南四湖流域。
Abstract: Currently many studies have been conducted to analyze the impact of urbanization on the change of stream structure.However,most of them have concentrated on some developed areas,but the less developed urban areas have attracted few atten-tions. Taking Nansi Lake Basin as the investigation area,this study analyzed the change of stream structure during the urbanizationprocess. The change of land surface was firstly extracted by using remote sensing images of 1987,2000,and 2014. Based on thestream structure data derived from topographic maps in 1980s,2003 and 2014,this study further analyzed the effect of urbanizationon spatiotemporal change of stream structure in 30 years by adopting indicators of quantity,structure and connectivity,respectively.The results show that: ( 1) The construction land increased by 1568.06 km2during the past 30 years. The area of urban construc-tion land has grown significantly since 2000. The percentage of urban population was 32% in 2012. ( 2) The whole river length,ar-ea and river density percentage have decreased by 135.46 km,2.75 km2and 0.49 km / km2,respectively during the study period.In addition,the impact of urbanization on stream structure varied spatially across the study area. The rivers at the low level experi-enced more significant change,while the water surface rates increase by 59.79% continuously. ( 3) Although the spatial pattern ofstream remained unchanged,the stream structure varied significantly during the study period. The stability value of river networkdecreased by 4.30%,and the connection rate and the combination degree fell by 21.82% and 21.62%,respectively. Moreover,theurban expansion intensity has strong-positively impacted on the stream. The study helps in better understanding the impact of urban-ization on stream structure at different spatial scales and urbanization levels,as well as to provide a valuable support and referencefor stream protection.
Keywords: Urbanization; stream structure; land surface change; Nansi Lake Basin.
城市化进程中下垫面性质的变化使得大量河流水系遭到破坏,进而引发一系列水资源与水环境问题,严重制约了城市和流域的可持续发展[1-2]. 目前,国内关于城市化对水系河网演变影响的研究主要集中在高度城市化地区的城市或城市群流域尺度,如上海[3-5]、深圳[6-7]、杭州[8]等城市流域,以及太湖[9-12]、长三角[13]等城市群流域。 这些地区面临的共性问题和研究成果为: 近 30 年来城市不透水面积剧增,河网水系和水环境在快速城市化进程中承受了巨大的压力,一方面河网结构趋于简单化、主干化,河湖面积萎缩,连通度下降,河流健康受到严重损害; 另一方面河流滞蓄洪涝水与水质净化能力明显下降,洪涝灾害以及河流水质恶化问题严重。
城市化对水系河网的影响具有明显的区域性和阶段性特点,探索不同流域尺度、不同城市化背景下流域水系的时空特征,能更好地制定规划工作,为后期河网保护与管理、水资源利用与可持续发展、构建生态城市提供参考依据。 目前流域尺度下对水系河网演变的研究较少,仅有对快速发展的太湖流域、长三角地区的研究,而对其他城市化背景下流域水系演变的研究较少。
南四湖是一个复杂的大流域,是南水北调东线的重要调节湖泊之一,也是干旱和洪水频繁发生的流域。流域内水系纵横交错,而城市化刚进入加速发展阶段,水系受自然和人为干扰发生较大改变。 结合城市化进程,定量分析流域河网水系的变化过程,探讨其变化因素,其成果可以补充城市化对水系结构影响的研究案例,也可以为南四湖流域的水资源管理与调蓄、防洪抗旱减灾、流域宏观治理和规划等研究提供参考。
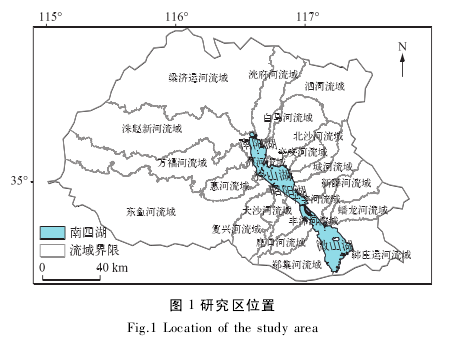
1 研究区概况。
南四湖流域( 34°24'~35°59'N,114°52'~117°42'E) 是淮河流域的子流域,从鲁西南部地区向南延伸至苏北地区,范围北起大汶河南岸,南抵废黄河南堤,东至鲁中南低山丘陵区西侧边缘,西以黄河堤坝为界。 南四湖是由北向南连续分布的微山湖、昭阳湖、独山湖、南阳湖 4 个相连湖的总称,湖区相互之间由自然和人工河道相连,是我国第六大淡水湖,也是南水北调东线工程中的重要调蓄水库之一。 流域包含 21 个子流域,总面积为 3.17×104km2,其中水域面积约 1266 km2( 图 1) . 全流域以京杭大运河和南四湖为界,湖东为鲁中南低山丘陵和山前冲洪积平原,河流大多属于洪水型季节性河流,源短流急,洪水势猛而峰高; 湖西为黄河中下游冲击而成的黄泛平原,大多河流为坡水型河流,河道宽浅,集流入湖缓慢,洪水量大而峰低。 流域入湖大小河流合计 53 条,年平均入湖径流量为 29.6×108m3,年平均出湖径流量为 19.2×108m3. 由湖西入湖的河流有 25 条,由湖东入湖的河流有 28 条。