摘 要
本文从分项收入来源视角研究个人所得税为完善个税税制提供建议。收入按照收入来源可以分为工资性收入、经营性收入、财产性收入和转移性收入。本文基于2011-2017年个人所得税数据,测算个税分项收入占比和税收负担,发现在居民收入来源日益多样化的背景下,个税仍然以工资薪金为主。个人所得税结构不合理。个人所得税的分类征收制度加剧了个人所得税收入结构的扭曲。

MT指数证实分类征收模式下个税的收入分配效果有限。因此,需要加快推进分类征收模式向综合和分类相结合征收模式转变。依据个税分项征收模式,推导出基尼系数按收入构成的分解方法以分析个税对分项收入的调节作用。实证发现个税对经营性收入的调节作用较为明显。
将影响MT指标的平均税率和累进性按照收入来源进行分解。结论是工资性收入税负过低造成个税平均税率低。财产性收入和经营性收入税负高。经营性收入税负对平均税率贡献最大。经营性收入和工资性收入累进性高,财产性收入累进性低。经营性收入累进性对总体累进性贡献最大。个税主要通过经营性收入发挥收入分配效应。
个税主要调节了经营性收入的结论与实际不符。探究原因,发现财产性收入和经营性收入名义税负远高于实际税负。说明经营性收入与财产性收入“跑冒滴漏”现象严重。因此个税过于依赖工资性收入。经营性收入与部分财产性收入采用自主申报的征税方式,信息不对称,征管不足和居民纳税意识薄弱都是税收流失严重的原因。财产性收入构成相对复杂。进一步分析发现房屋租金收入是居民财产性收入的主要来源。
为此,本文提出了完善个人所得税制的建议。从收入结构上看,政府应该创造条件让更多群众拥有财产性收入和经营性收入。从个人所得税制度设计上看,将经营性收入纳入综合所得,采用综合征收模式。财产性收入沿用分项征收模式。房屋租金收入采取累进税制。从税收征管上看,一方面要建立现代化税务信息系统和提高税务人员纳税服务水平,提高税务机关征管水平;另一方面要加大税收处罚力度和提高居民纳税意识,促使居民自主申报。从房屋租赁市场开始试点,完善房屋租赁备案信息。
关 键 词: 个人所得税;收入分配;分项收入;累进性;平均税率。
ABSTRACT
This article studies personal income tax from the perspective of itemized income sources to provide suggestions for improving the tax system. According to the source of income, income can be pided into wage, operating income, property income and transfer income. Based on personal income tax data from 2011 to 2017, this paper estimates inpidual tax structure and itemized income tax burden. The results show that in the context of perse sources of income, personal income taxes are still dominated by wages.Thus ,the personal income tax structure is unreasonable. The classification system of personal income tax has exacerbated the distortion of the source structure of personal income tax .
The MT index confirms that under the classified collection model the income distribution effect of personal income tax is limited. Therefore, it is necessary to accelerate the transition from the classified collection to a comprehensive and classified collection. Based on the itemized collection mode, the decomposition method of the Gini coefficient according to income composition is derived to analyze the distribution effect of the tax on itemized income. The empirical findings show that the distribution effectof inpidual income tax on operating income is more obvious.
Decompose the average tax rate and progressiveness that affect MT indicators according to the source of income. The conclusion is that the low tax burden on wage causes a low average tax rate. The tax burden on property income and operating income is high. Operating income tax burden contributes the most to the average tax rate. Operating income and wage income are both highly progressive 。But the progressiveness of property income is low. The progressiveness of operating income contributes the most to the overall progressiveness. Therefore, the personal income tax mainly exerts the income distribution effect through operating income.
The conclusion that the personal income tax mainly regulates operating income is inconsistent with reality.Investigating the reasons, it was found that the nominal tax burden on property income and operating income was much higher than the actual tax burden. This shows that the phenomenon of tax evasion of operating income and property income is serious. Therefore, the tax is too dependent on wage. The operating income and part of the property income are taxed by self-declaration. Asymmetric information, Inadequate tax collection and weak tax consciousness of residents are the reasons for the serious tax loss.The composition of property income is relatively complex. Further analysis found that housing rent is the main source of property income.
To this end, this article puts forward suggestions to improve the personal income tax system. From the perspective of income structure, the government should create conditions for more people to have property income and operating income. From the perspective of the design of the personal income tax system, the operating income is included in the comprehensive income, and the syndrome income model is adopted. Property income follows the itemized collection mode. Rent adopts a progressive tax system.From the perspective of tax collection and management, on the one hand, we must establish a modern tax information system and improve the service level of tax personnel to improve the level of tax collection and management; on the other hand, it is necessary to increase tax penalties for tax evasion and increase residents' awareness of tax ,so as to encourage residents to declare taxes in accordance with the law. It is reasonable to improve housing leasing record system to pilot the leasing market.
KEY WORDS: Personal income tax; Income distribution; Itemized income; Progressive; Average tax rate。
1、绪论
1.1、研究背景及研究意义。
1.1.1、研究背景。
改革开放的40多年间,我国逐渐从计划经济体制转变为社会主义市场经济体制。
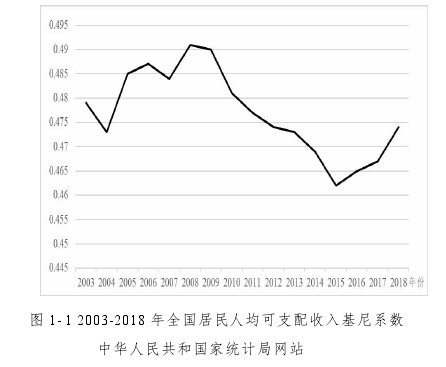
这极大地提高了资源配置效率,促进了经济发展,改善了人民生活。但是市场配置资源更加注重效率,在一定程度上忽视了公平。同一个国家,一部分人挥金如土,另一部分人却还在为温饱问题发愁。基尼系数是衡量收入不平等的一个常见指标。国家统计局公布的数据如图1-1所示。
2003-2018年基尼系数在0.46-0.49之间上下波动。较高的基尼系数表明我国收入差距过大。过于悬殊的贫富差距则会激化社会矛盾,威胁社会稳定。面对我国收入差距现状,政府应该制定相应的政策,缩小收入差距。
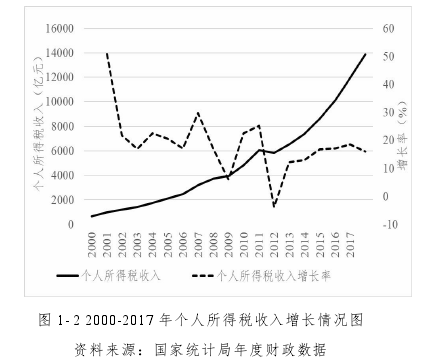
个人所得税对居民收入直接征税,具有难以转嫁的特点。因此, 个税成为各个国家调整收入分配的重要工具。从图1-2可以看出,2000年以来,中国个人所得税收入增长迅速。除了改革的特殊年份,个税收入年增长率均在20%左右。
2018年个人所得税收入达到13872亿元,环比增长15.89%。个人所得税已经成为仅次于增值税、企业所得税的第三大税种,占全国税收总收入的8.7%。
随着个税规模扩大,个税对居民收入的影响增大。但是我国个人所得税税制存在许多的不足,未能较好的发挥调节收入分配的功能。为此,国家曾多次进行个人所得税改革,完善税制。
2018年个税改革将工资薪金、劳务报酬、稿酬和特许权使用费纳入综合所得进行综合征税,个体工商户生产经营所得和企事业承包承租经营所得合并为经营所得,开始迈向综合与分类相结合征收模式。但是其他应税项目依旧采取分项减除、分项计征的征收模式。税制改革仍然有较大空间。今后的改革中哪些项目进行综合征收?哪些项目分类征收?需要对个税分项收入进行实证研究,为迈向更广泛的综合税制提供数据支持。
1.1.2、研究意义。
从理论意义上看,本文利用数据定量分析我国个税存在的问题。个人所得税的收入分配效应是各分项收入综合作用的结果。本文建立了平均税率及累进性按照收入来源分解的数学模型,分析了个税对分项收入的调节情况,从而为个税改革提供实证依据。
税收和转移支付是调节收入分配的两大工具。中国没有调整存量资产的财产税,也没有开征调节居民收入代际传递的遗产税。且根据刘怡和聂海峰(2004)的实证结果,我国增值税、消费税、营业税等间接税具有一定的累退性质,会加大居民收入差距。在此背景下,个人所得税需要肩负起调节收入分配差距的重任(贾康和梁季,2010)。因此,从现实意义上看,研究个人所得税分项收入有利于完善个人所得税制,发挥个税调节收入的功能,缩小收入差距,促进社会和谐发展。
【由于本篇文章为硕士论文,如需全文请点击底部下载全文链接】
1.2、文献综述.
1.2.1、评价个人所得税收入分配效应
1.2.2、改革税制要素增强个人所得税的收入分配效应 .
1.2.3、从收入来源考察个人所得税收入分配效应.
1.2.4、国内外研究评述
1.3、研究内容与方法.
1.4 、创新与不足.
2、分项征收模式下个人所得税现状
2.1、 个人所得税分项收入及结构变动情况.
2.2 、居民可支配收入和结构变动情况,
2.3、个税收入与居民可支配收入对比分析.
2.4 、个税结构不合理.
3、个人所得税的收入分配效
3.1、 个税收入分配效应的含义和衡量指标.
3.2、个 税收入分配效应的影响因素分解.
4、个人所得税的收入分配效应实证分析
4.1、数据选取和处理
4.2、 个人所得税收入分配效应微弱.
4.3、个人所得税对经营性收入再分配效应明显
4.4、小结.
5、个人所得税收入分配效应的实证分解结
5.1 、平均税率过低造成个人所得税收入分配效应微弱
5.2 、平均税率按照收入来源进行分解.
5.3 、累进性按照收入来源分解.
5.4、 小结.
6、税收流失削弱个税收入分配效应
6.1 、经营性收入和财产性收入税收流失严重.
6.2、税收流失原因分析.
6.3 、进一步分析财产性收入。
6.4、小结
7、结 论
创造性将初次分配和再分配结合在一起分析,从调整收入结构和个税税制两个角度为提高个税的收入分配效应提供建议。
分析个人所得税三大分项收入占比及税负水平,可做如下总结:经营性收入税负低,且下降;工资性收入税负中等,呈上升趋势;财产性收入个税税负高,呈下降趋势。个税结构不合理,工资性收入占比过高,财产性收入和经营性收入个税征税不足。
MT指标表明个税的收入分配效应微弱。将基尼系数按照收入来源角度分解,发现财产性收入不平等程度大,经营性收入不平等程度扩大,工资性收入分配相对公平。转移性收入没能起到降低收入差距作用。且个税对经营性收入的分配效应明显,对其他收入的作用不显着。
MT指标的分解结果显示平均税率过低造成个税的收入分配效应微弱。分类征收模式下,不同收入适用不同的税率和扣除额,因此不同来源收入的累进性和税负不同。实证表明工资性收入税负过低造成个税平均税率低。经营性收入和财产性收入税负高。经营性收入和工资性收入累进性高,且两者相差不大。但是财产性收入累进性低。因此,两者相结合,在没有偷漏税情况下,个税对经营性收入调节效果最显着。
文章的另一个特点是将名义税负和实际税负进行比较,大致估计了税收流失情况,并分析了税收流失的原因。数据表明:现实生活中超过一半的财产性收入和经营性收入个税未能征收。这是个税结构不合理的原因之一,也极大地削弱了个税的收入分配效应。部分财产性收入和经营性收入需要自己主动上报纳税信息。经营性收入和财产性收入来源分散,信息复杂难以核实,征管难度大,给予了纳税人逃税的空间。而工资薪金以代扣代缴方式征税,偷税漏税隐瞒不报行为较少。居民纳税意识薄弱,征管能力不足和被动的征管态度都是造成税收流失的原因。偷税漏税行为会极大降低实际税负和累进性进而影响个税的收入分配效应。因此要减少信息不对称,加强税收征管。
财产性收入来源多样化。因此,对财产性收入的进一步分析。结果显示房屋租金收入是财产性收入主要来源,且增长迅速。调节财产性收入关键是调节房屋租金收入。
参考文献.


