摘要
财政政策是各国政府“熨平”经济波动的重要手段,也是促进区域协调发展最为有效的经济政策。自二十世纪 70 年代以来,中国开始进行经济体制改革开放,采取了梯队推移式的政策方法和以“允许一部分人先富起来的”非均衡发展策略,这一做法虽然使我国经济获得了快速发展,但也造成了严重的区域发展不平衡,主要表现为我国东部地区与其他地区的经济发展水平相差过大。
中国在当前财政分权的框架之下,各个地区都存在着鲜明的经济特征,使用相同的财政政策必然不能满足各个地区经济发展的需要。适度的经济差异可以形成经济落差,带动落后地区发展,有利于资源配置和整个国家的经济发展,但我国的区域经济差异已经超出了适度的范围,区域差异过大不仅影响人民的生活福利,更有可能引发严重的社会问题,因此财政政策效应的区域差异问题也成为我国经济学家近年来重点研究的课题之一。
本文将全国划分为东中西部和东北地区,选取 1992 年至 2017 年全国财政收入(主要指税收收入)、全国财政支出和四大经济区的 GDP 来建立结构向量自回归模型(即 SVAR 模型)以及结构脉冲响应函数,分析发现我国财政政策的效应确实存在明显的区域差异,并通过方差分解进一步发现财政政策工具执行效果的差异是造成财政政策区域效应的原因之一。文章联系我国的实际发展情况,总结出我国财政政策产生区域效应的原因,包括东、中、西、东北四个地区区域经济发展不平衡和财政政策工具本身存在缺陷,缺陷主要为税收政策不合理和转移支付制度不规范。
文章通过借鉴德国、美国、英国改善财政政策区域效应的经验方法,对我国财政政策运用的思路提出了以下政策建议,一是对财政政策进行全方位统筹把控。包括立足于区域经济发展不平衡的现实实行差异化财政政策、合理把握财政政策介入、调整与退出的时机选择和通过有效整合来确保财政政策的支持效果。二是优化税制结构和调整税收优惠形式。三是规范转移支付制度。包括规范转移支付制度的分配方式、增加横向转移支付模式、合理确定政府的事权和财权与建立健全完善的财政法制体系。
关键词: 财政政策;效应;区域差异;结构向量自回归模型 。
Abstract
The fiscal policy is an important measure for moderating economic fluctuation, and an effectual economic policy to promote the harmonious growth of the regional economy. Since the 1970s, China has begun to reform and open up its economic system.It has adopted a step-by-step policy approach and a non-balanced development strategy of "allowing some people to get rich first". This practice has resulted in a serious regional imbalance in the rapid development of China's economy, which is mainly manifested in the economic development of Eastern China and other regions. The difference is too large.
Under the current framework of fiscal decentralization in China, there are distinct economic characteristics in all regions. The use of the same fiscal policy will inevitablynot meet the needs of economic development in all regions. Moderate economic disparities can form economic disparities, promote the development of backwardregions, and benefit the allocation of resources and the economic development of the whole country. However, the regional economic disparities in China have gone beyondthe scope of moderation. Excessive regional disparities not only affect people's welfare, but also may cause serious social problems. Therefore, the regional disparities of fiscal policy effects have become our economy. Economists in recent years focus on one of the topics.
This paper divides the whole country into the eastern, central ,western and northeastern. The structural vector autoregressive model (SVAR model) and thestructural impulse response function are established by choosing the national fiscal revenue (mainly tax revenue), the national fiscal expenditure and the GDP of the four economic regions from 1992 to 2017. The analysis shows that there are obvious regional differences in the effect of fiscal policy in China, and the variance score is used.
It is further found that the difference in the implementation effect of fiscal policy instruments is one of the reasons for the regional effects of fiscal policy. Based on the actual situation of China's development, this paper sums up the reasons for the regional effects of China's fiscal policy, including the imbalance of regional economic development in the four regions of East, Central, West and Northeast, and the defects of financial policy instruments themselves, mainly due to the unreasonable tax policy and the irregular transfer payment system Based on the experience of Germany, the United States and the United Kingdom in improving the regional effects of fiscal policy, this paper puts forward the following policy suggestions for the application of fiscal policy in China. Firstly, overall control of fiscal policy should be carried out. It includes the implementation of differentiated fiscal policy based on the reality of unbalanced regional economic development, reasonable grasp of fiscal policy intervention, timing of adjustment and exit, and effective integration to ensure the support effect of fiscal policy. The second is tooptimize the structure of tax system and change the form of tax preferences. Third, standardize the transfer payment system. It includes standardizing the distribution mode of transfer payment system, increasing the horizontal transfer payment mode, reasonably determining the government's power and financial power, and establishing and perfecting the financial legal system.
Key Words: fiscal policy; effects; regional differences; structural vector autoregressive model。
第一章 绪论
第一节 研究的背景和意义 。
一、研究的背景 。
众所周知,财政政策是国家进行宏观调控的主要手段之一。自 2008 年由美国次贷危机引发全球金融危机后,各国的经济都受到了严重冲击,中国的经济发展速度也出现了明显的下滑倾向。为刺激经济回暖,国家自 2008 年 9 月开始连续实施了多年积极宽松的财政政策,充分发挥了财政政策的职能作用。
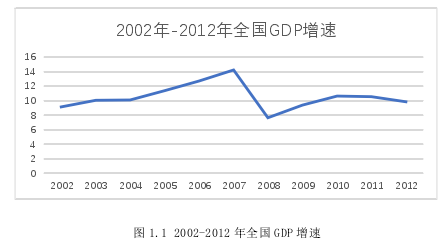
如图 1.1 所示,2008 年我国 GDP 增速仅为 7%1,而到 2010 年时,我国 GDP 增速已稳定至 10%以上,在全球率先实现了经济形势的总体回升,GDP 也一跃升至世界第二位,各个经济指标都实现稳定增长,充分说明我国财政政策发挥了良好的效果。
但从 1978 年开始,我国由于实行经济体制改革,实施了一系列优先推进东部发展的经济政策,东部沿海固然为我国整体经济的发展做出了重大贡献,但也由此带来了严重的区域发展不平衡。在当前先行的财政政策下,区域经济的差距还在不断拉大,成为我国当前面临的重点问题之一。
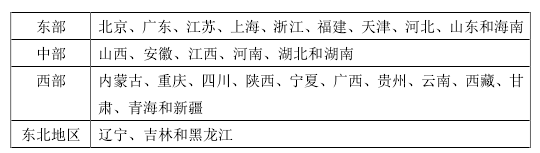
2015 年国家统计局重新颁布了对经济区域的划分方式,将全国分为东部、中部、西部以及东北四大经济区域,具体划分方式如表 1.1 所示:
表 1.1 我国经济区域划分方式 。
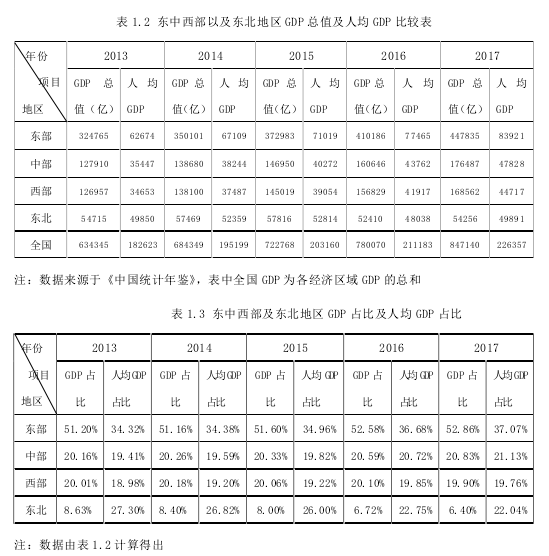
为了从总体上更直观的分析这种区域发展不平衡,我们选取近 5 年内四大经济区域的 GDP、人均 GDP 以及 GDP 增长率等经济指标为观察对象,进行分析。
如表 1.2 和表 1.3 所示,从 2013 年到 2018 年,四大经济区域的 GDP 与人均GDP 均呈现出上涨的趋势,但各个区域之间均存在不小的差距。一、从 GDP 的角度来看,近 5 年来东部地区 GDP 远超中西部和东北地区,GDP 达到全国 GDP 的50%2以上,中部、西部和东北地区的 GDP 占比依次排列。例如,在 2017 年,东部地区 GDP 占全国 GDP 的比重为 52.86%,东北地区占比为 6.4%,差距达到了46.46%,是近五年以来差距最大的一次;二、从人均 GDP 角度来看,东部地区的人均 GDP 和人均 GDP 占比情况均居于全国的最高水平,东北地区的 GDP 和 GDP 占比虽然处于末端,但人均 GDP 和人均 GDP 占比均超过了中西部,这与东北地区所含省份较少但经济发展情况较好有关。此外,东部地区人均 GDP 占比均在 30%以上,基本为西部地区人均 GDP 占比的 2 倍。如在 2017 年,东部地区的人均 GDP占比达到 37.07%,而西部地区人均 GDP 占比仅为 19.76%。以上,通过 GDP 和人均 GDP 等经济指标的比较可以看出,在现行的财政政策下,我国存在不小的区域经济差距,尤其是东部地区和西部地区。
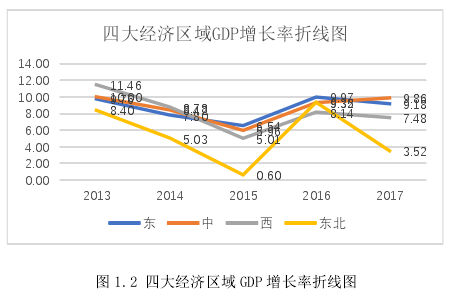
从 GDP 增长率来看,近 5 年来,东中西部以及东北地区的 GDP 增长率均有较大的波动,如图 1.2 所示,在 2013 年和 2014 年,中部和西部的增长速度均超过了东部地区,2015 年到 2017 年中,四个经济区域的 GDP 增速都处于稳定增长,到 2017 年时,中部地区的增长率为 9.86%,位于第一位。可见,在 GDP 增长率上,四个区域也呈现出明显的差异性。
综上所述,从 GDP、人均 GDP、GDP 占比、人均 GDP 占比和 GDP 增长率几个经济指标可以看出,四个地区的发展情况均存在不小的差距,东部地区的经济发展情况明显优于其他地区。财政政策本身是平衡经济波动的有效手段,是改善区域差异性的有效政策,但在同样的财政政策下,我国的区域经济差距却还在不断扩大,这也侧面证实我国的财政政策可能存在区域效应。我国已经进入中高速增长的新常态,在实现经济结构再平衡的过程中,也面临着增速换挡、产业转型等许多考验。这也就更需要我国进一步探索优化财政政策运用的思路和方法,充分发挥财政政策的宏观调控作用,协调区域经济发展。
【由于本篇文章为硕士论文,如需全文请点击底部下载全文链接】
二、研究的意义.
第二节研究内容与研究方法
一、研究内容.
二、研究方法.
第三节国内外文献综述
一、国外文献综述.
二、国内文献综述.
第四节创新与不足
二、不足之处.
第二章 财政政策效应区域差异研究的政策基础和理论基础.
第一节政策基础
一、税收政策
二、转移支付制度.
第二节理论基础
一、经济增长理论.
二、财政政策乘数效应理论.
第三章 我国财政政策效应区域差异研究的实证检验
第一节.变量选择与模型建立
一、变量设定.
二、模型选择.
第二节财政政策效应区域差异的实证分析
一、东部地区.
二、中部地区.
三、西部地区.
四、东北地区.
第三节财政政策效应区域差异的实证总结.
一、财政政策的效应存在明显的区域差异.
二、财政政策工具的实施效果存在区域差异.
第四章 财政政策效应存在区域差异的原因
第一节区域经济发展不平衡
一、东中西、东北地区经济发展水平比较.
二、区域经济发展不平衡导致财政政策效应的区域差异.
第二节财政政策工具存在缺陷
税收政策不合理.
二、转移支付制度不规范.
第五章 改善财政政策效应区域差异的国际经验与借鉴
第一节国外改善财政政策效应区域差异的做法
一、美国
二、德国.
三、英国.
第二节国外改善财政政策效应区域差异的经验借鉴
一、转移支付制度的经验借鉴.
二、税收政策的经验借鉴.
第六章 改善我国财政政策效应区域差异的政策建议.
第一节对财政政策进行全方位统筹把控
一、立足于区域经济发展不平衡的现实实行差异化财政政策.
二、合理把握财政政策的介入、调整与退出的时机选择.
三、通过有效整合来确保财政政策的支持效果.
第二节.优化税制结构和调整税收优惠形式.
一、优化税制结构.
二、调整税收优惠政策
第三节规范财政转移支付制度
一、规范转移支付制度的分配方式
二、增加横向转移支付模式.
三、合理确定政府的事权与财权.
四、建立健全完善的财政法制体系
健全完善的财政法制体系是所有财政政策得以有效的保障。发达国家对建立财政体制的法律体系十分注重。例如美国通过的《财政预算法》,德国先后制定了《基本法》和《财政平衡法》等在内的一整套财政法律规范,均明确划分了各级政府的事权与财权。同时还在法规中给予了财政部或专门的机构委员会对标准提出修改和建议的权利,具有规范性和灵活性的同时保障了制度的准确度和科学性。
我国的转移支付制度在这一方面规定还比较笼统,很多规定都只是设定一个大概范围,需要借鉴美国和德国的经验做法。一是要给予财政转移支付以法律地位,明确各利益主体,清晰划分各级政府之间的事权与财权,以法律形式为转移支付提供法律保障;二是要加快转移支付的的立法进程,对财政转移支付的政策目标、核算标准等作出明确规定,制定相关的法规和制度,确保转移支付制度政策到位、有法可依;最后是要加强对制度执行过程中的法律监督,并完善监督约束机制和责任追究制度。
参考文献.